Fig 3.
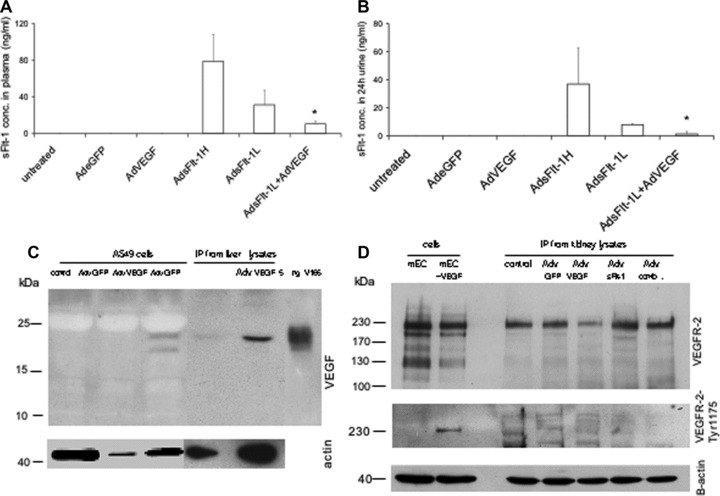
Quantitative measurement of mouse sFlt-1 by ELISA and detection of VEGF-A and VEGF-R in mice. In mice either untreated (n= 4) or treated with Adv for eGFP (n= 4) or AdvVEGF (n= 6) endogenous sFlt-1 concentrations are under the detection level in plasma (A) and in urine (B). Mice treated with high concentrations of Adv for sFlt-1 (5–7,5 × 109 pfu, n= 10) show extremly high concentrations and mice treated with lower levels, which were also used for rescue experiments (2,5–3,5 × 109 pfu, n = 10) have a reduced level for sFlt-1 in plasma and urine. Rescue experiments with AdsFlt-1 and AdVEGF (1 × 108, n = 4) have significant reduced levels in plasma und urine. Data are mean (±SEM) of several mice used for each experiment. *P < 0.05 as compared with low-dose sFlt-1- (AdsFlt-1- L) treated mice. Representative detection of VEGF-A (C) and VEGFR-2/FLK-1 (D) in adenovirus-treated cells and mice by reducing Western blot. To detect VEGF-A 1 mg cell lysates was used for IP. For IP from kidney lysates 5 mg total protein was immunoprecipitated with an anti-VEGF-A monoclonal antibody. As positive control 5 ng rh VEGF-A (isoform 165 from insect cells) was used directly. For sample loading beta-actin was detected by immunoblotting for the same blot with an appropiate antibody. To detect the VEGFR-2/Flt-1 total protein or the phosphorylated protein, 20 μg cell lysates from mouse endothelial cells either unstimulated or stimulated with VEGF-A (50 ng/ml over 10 min) was loaded directly on the gel. For IP from kidney lysates 2 mg of total protein was immunoprecipitaed with an anti-mouse VEGFR-2 antibody and immunoblotted with the same antibody. For detection of phosphorylated mouse VEGFR-2 400 μg cell lysates and 4 mg kidney lysates were used for IP followed by immunoblotting with an antibody for phospho-VEGFR-2-Tyr1175. For sample loading beta actin was detected by using 40 ug lysates from each samples for immunoblotting with an appropiate antibody.
