FIGURE 2.
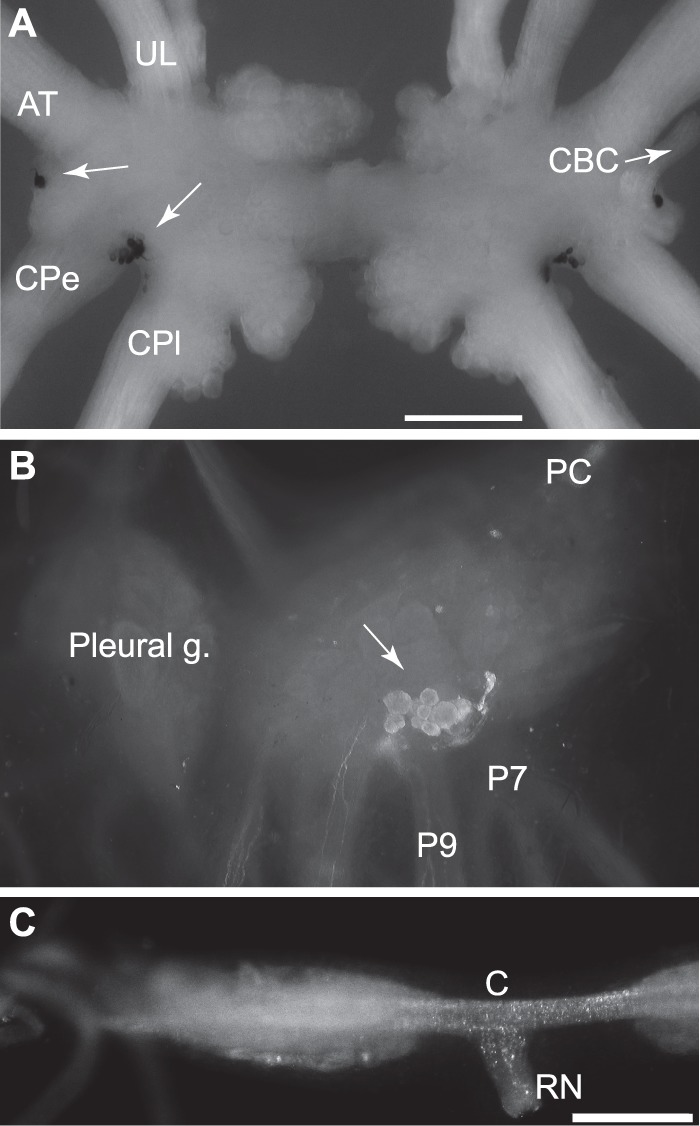
Localization of expression of apALNP and apFLNP. A, in situ hybridization shows that apFLNP (YAEFLa) mRNA is expressed on the ventral surfaces of the cerebral ganglion. A single neuron is located in the E cluster near the root of the cerebral-buccal connective (CBC and white arrow, only present at the right. The left CBC was accidentally cut.), and a cluster of small neurons is located between the roots of the cerebral-pedal connective (CPe) and cerebral-pleural connective (CPl). White arrows point to the labeled cells at the left side. AT, anterior tentacular nerve; UL, upper labial nerve. Calibration, 500 μm. B and C, immunocytochemistry with GdFAD antibody. B, dorsal surface of the pedal ganglion. The cluster of positive neurons matched in situ hybridization with apALNP, suggesting that GdFAD antibody can label apALNP-positive neurons. C, buccal ganglion. Consistent with in situ hybridization, there are no GdFAD-positive somata in the buccal ganglion, but there are GdFAD-positive fibers and varicosities, e.g. in the neuropile, commissure (C), and the radula nerve (RN). Presumably, the staining suggests that apALNP-positive fibers and varicosities are in the buccal ganglion. Calibration, 500 μm.
