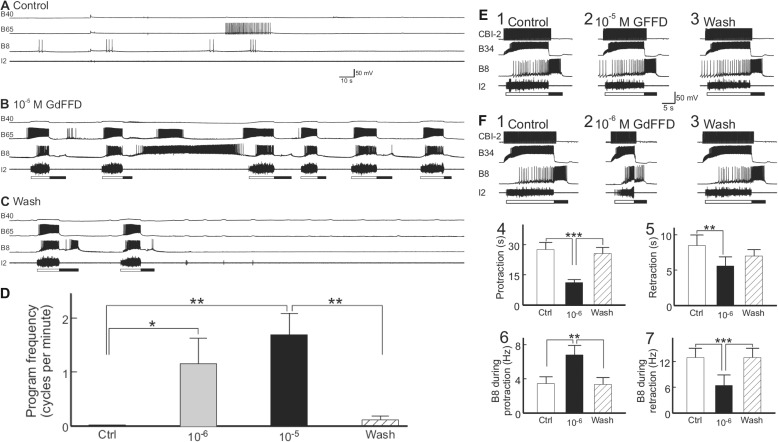
FIGURE 8.
GdFFD induces cyclic activity in the buccal central pattern generator. Each cycle of programs consists of a protraction (open bar, marked by I2 nerve activity) − retraction (closed bar, marked by hyperpolarization of B65 interneuron) sequence. A, control: at rest, there was little activity in the buccal CPG protraction interneurons B40 and B65, radula closure motoneuron B8, or the I2 nerve. B, during the perfusion of 10−5 m GdFFD, the feeding network became cyclically active. The motor programs induced were mostly egestive because B8 activity occurred during the protraction phase (represented by B65 bursting). Consistently, B40, a neuron important for ingestive programs, was not active, although it received cyclic synaptic inputs. C, after washout of the peptide, the preparation gradually returned to the inactive state, beginning with the trace, 4.2 min after the start of the washout. D, summary data (n = 4) showing the effects of 10−6 and 10−5 m GdFFD on the activity of the buccal CPG. The frequency of the motor programs is the number of cycles per min measured over a period of 7 min or more in each experimental condition. Both 10−6 and 10−5 m GdFFD increased the frequency of spontaneously occurring motor programs. Bonferroni post hoc test (with selected comparisons between peptide applications versus the control (Ctrl) or the wash) is as follows: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. Error bars represent S.E. E and F, effects of GFFD and GdFFD on motor programs elicited by the command-like interneuron CBI-2. B34 is a buccal protraction interneuron active during protraction (open bar, marked by I2 nerve activity); CBI-2 is an interneuron that triggers programs by activating protraction interneurons in the buccal ganglion, which, in turn, activate the retraction neurons. In addition, CBI-2 receives inhibitory feedback during retraction (65), and it is not or only weakly active during retraction. Thus, single cycle motor programs were elicited by stimulation of CBI-2 at 9 Hz throughout the protraction phase with inter-trial intervals of 1 min. E1–3, representative examples. E1, control: CBI-2 stimulation induced an ingestive motor program, in which B8 was predominantly active during retraction (filled bar, marked by hyperpolarization of B34 interneuron). E2, perfusion of 10−5 m GFFD had no obvious effect on the CBI-2-elicited program. E3, washout of the peptide. F1–3, representative examples. F1 and F3 are the same as E1 and E3, except with the perfusion of (F2) 10−6 m GdFFD, which increased B8 firing during protraction and reduced B8 firing during retraction. It also decreased the duration of protraction. F4–7, group data (n = 4) showing the effects of GdFFD on (F4) protraction duration, (F5) retraction duration, (F6) B8 activity during protraction, and (F7) B8 activity during retraction. Bonferroni post hoc test is as follows: **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.