FIGURE 4.
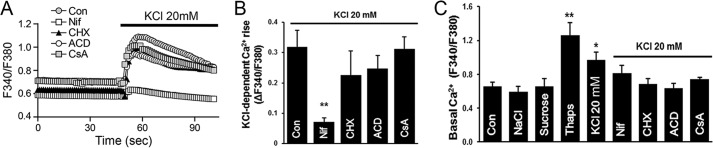
Ca2+ dynamics in response to acute KCl depolarization of A7r5 cells. Cells were loaded with Fura 2-AM and bathed in Ca2+-containing HBS. Imaging was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” A, acute membrane depolarization by K20 results in a global rise in intracellular Ca2+, which is inhibited by Nif (10 μm) but not by ACD (10 μm), CHX (10 μg/liter), or CsA (10 μm). Traces represent average fluorescence intensity of 15–20 individual cells. B, quantitation of the K20-induced Ca2+ rise as maximal Fura-2 ratio from base line (ΔF340/F380, n = 4–6; **, p < 0.01). C, basal intracellular Ca2+ levels were significantly increased in A7r5 cells after 24 h exposure to K20 or 1 μm Thaps. The osmolarity controls NaCl and sucrose did not alter resting Ca2+ levels in A7r5 cells. The addition of Nif (10 μm), CHX (10 μg/liter), ACD (10 μm), or CsA (10 μm) before depolarization by K20 prevents the elevation of basal Ca2+ level (n = 3–12; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01). Error bars, S.E.
