FIGURE 1.
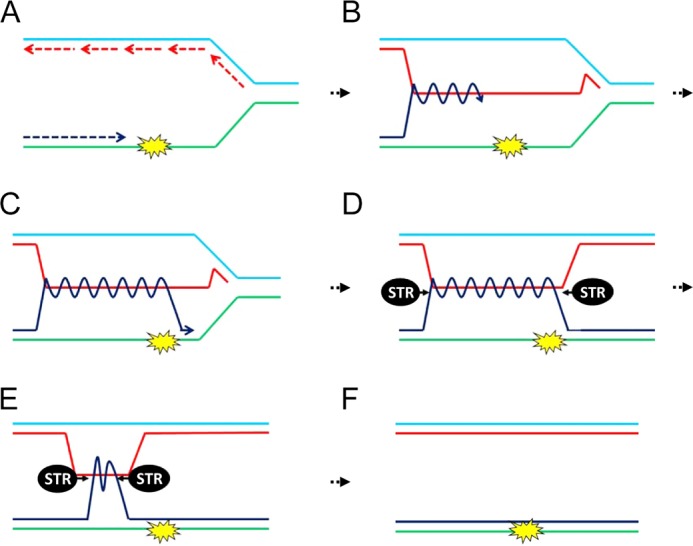
Bypass of a replication-stalling lesion through the use of Rec-X-based template switch recombination (after Liberi et al. (13)). A, a replication fork is shown with the nascent leading strand (dark blue) encountering a stall-inducing lesion. B, the leading strand switches to use of the nascent strand of the sister chromatid as a template, bypassing the lesion. C, the leading strand returns to its original template. D, a Rec-X intermediate, which is resolved by the STR complex (E and F). A Rec-X could also form during the repair of gapped DNA left behind an advancing replication fork (not shown).
