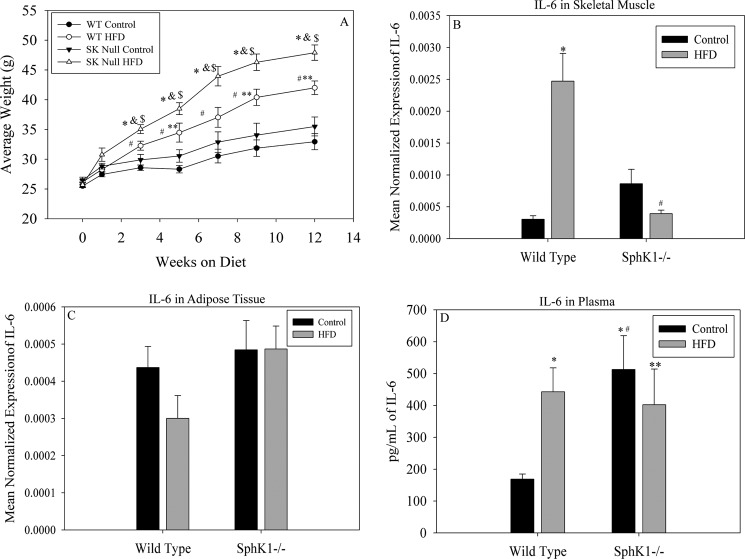
FIGURE 6.
Diet-induced obesity promotes Il-6 expression in skeletal muscle and is attenuated in Sphk1−/− mice. Eight-week-old male C57Bl/6J and Sphk1−/− mice were maintained on obesogenic or low-fat control diets for 12 weeks. A, mice maintained on the diets were weighed biweekly. Data are presented as average weight ± S.E., n ≥ 4 mice per diet group; #, p < 0.01 versus wild type control; *, p < 0.01 versus Sphk1−/− HFD; **, p < 0.05 versus Sphk1−/− control; &, p < 0.05 versus wild type HFD; $, p < 0.01 versus Sphk1−/− control. B, total skeletal muscle was removed from the hind limbs of diet-fed mice. Il-6 expression was evaluated using qPCR, *, p < 0.05 versus WT control; #, p < 0.01 versus WT HFD. C, adipose tissue was removed from the abdomen of mice maintained on the diet and Il-6 expression was determined by qPCR. All qPCR data in B and C are presented as mean normalized expression (n = 4) ± S.E. D, plasma was isolated post-mortem from diet-fed mice and analyzed for IL-6 content via Bioplex 2200 System assay. Data are presented as mean picograms of IL-6/ml of plasma ± S.E., n ≥ 4 mice per diet group; **, p < 0.05 versus WT HFD; #, p < 0.05 versus Sphk1−/− HFD; *, p < 0.05 versus WT control.