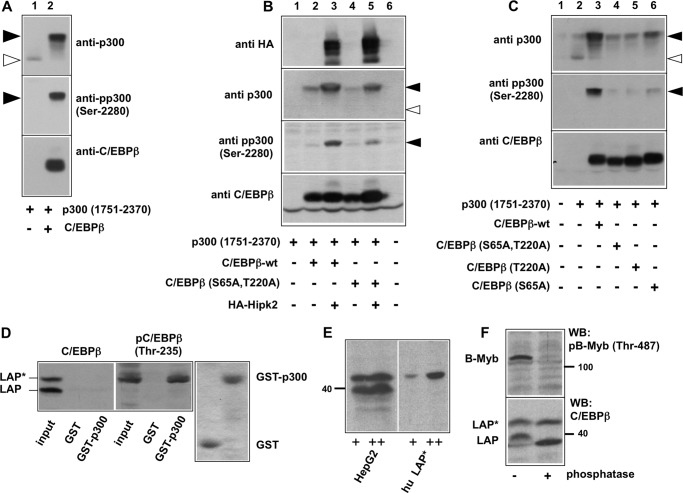
FIGURE 6.
Mutation of Hipk2 phosphorylation sites affects the C/EBPβ-dependent phosphorylation of p300. A--C, QT6 cells were transfected with the expression vectors indicated below the lanes. Total cell extracts were prepared 24 h after transfection and were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with antibodies against p300, phospho-p300-(Ser-2280), C/EBPβ, and the HA tag, as indicated. The unphosphorylated and phosphorylated forms of p300 are marked by white and black arrows, respectively. D, total cell extracts from HepG2 cells were incubated with Sepharose beads carrying GST or a GST-300-(1710–1891) fusion protein. Bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with antibodies against human C/EBPβ (left panel) or phospho-C/EBPβ (Thr-235) (middle panel). Control lanes show aliquots of the total cell extract (Input lanes). The LAP* and LAP isoforms of C/EBPβ are marked. The right panel shows a Coomassie Blue-stained gel to confirm equal loading of the Sepharose beads with GST and the GST-p300 fusion protein. E, total cell extract from human HepG2 cells and extracts from cells transfected with an expression vector for human LAP* were analyzed by SDS-Page and Western blotting with antiserum against C/EBPβ. F, cell extracts from human HepG2 cells were incubated with (+) or without (−) Fast AP phosphatase (Fermentas) for 2 h at 37 °C. Extracts were then analyzed by Western blotting (WB) using antiserum against C/EBPβ (lower panel). As control for the efficiency of the phosphatase treatment, we analyzed the phosphorylation of B-Myb using a phospho-specific antiserum against B-Myb phosphorylated at Thr-487 (top).