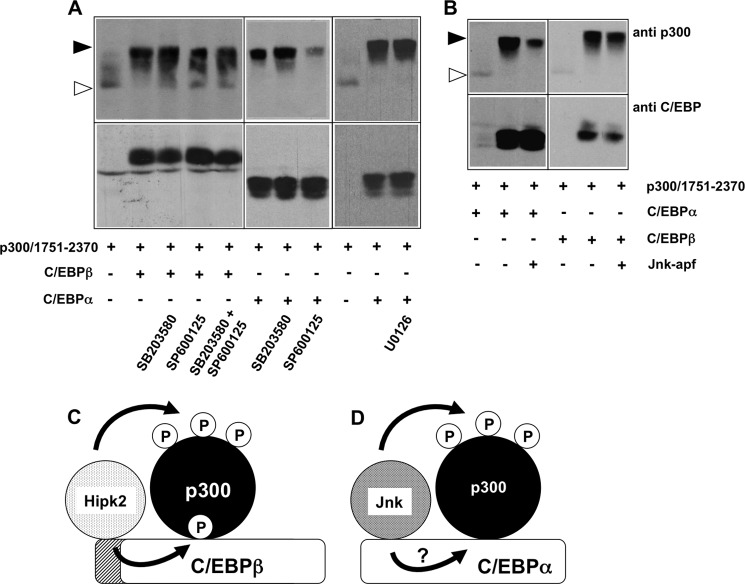
FIGURE 9.
Effect of kinase inhibitors on the C/EBPα- and C/EBPβ-induced phosphorylation of p300. A and B, QT6 cells were transfected as indicated at the bottom. Cells in panel A were additionally treated with the Jnk inhibitor SP600125 (40 μm), the p38 inhibitor SB203580 (15 μm), or the Mek1 inhibitor U0126 (10 μm) overnight before they were harvested. In panel B, Jnk-apf refers to a kinase-dead mutant of Jnk. Total cell extracts were analyzed after 24 h by Western blotting with antibodies against the p300 and the C/EBP proteins. The unphosphorylated and highly phosphorylated forms of p300-(1751–2370) are marked by white and black arrowheads, respectively. C, shown is a hypothetical model of the C/EBPβ-induced phosphorylation of p300. Hipk2 binds to the amino-terminal domain of C/EBPβ and phosphorylates C/EBPβ as well as p300 bound to C/EBPβ. Phosphorylation of C/EBPβ stimulates binding of p300; however, it is not known whether the phosphorylation affects the binding of p300 directly (as shown arbitrarily in this model) or indirectly, i.e. by inducing conformational changes in C/EBPβ. D, shown is a hypothetical model of the C/EBPα-induced phosphorylation of p300. C/EBPα triggers the phosphorylation of p300 by Jnk kinase. It is not known if Jnk binds directly to a specific domain of C/EBPα (as arbitrarily shown here) and whether Jnk also phosphorylates C/EBPα.