FIGURE 5.
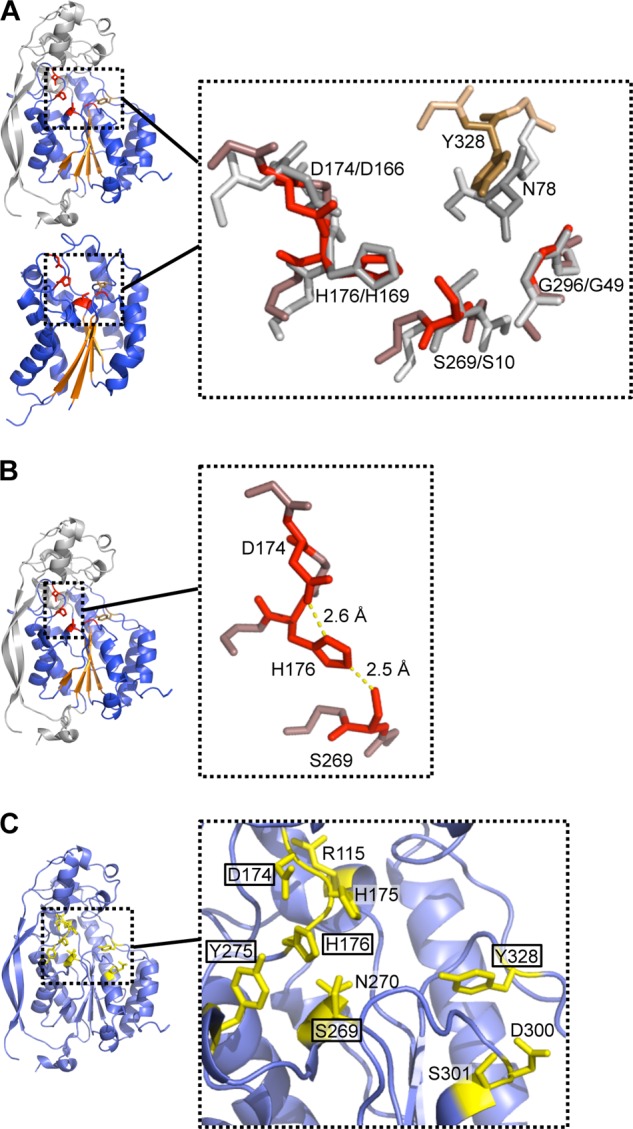
Architecture of the active site. A, superposition of the Asp-His-Ser triad and conserved Gly of AlgX (shown in red) and E. faecalis acylhydrolase/lipase (in gray). Asn and Tyr residues of E. faecalis acylhydrolase/lipase and AlgX, not used in the superposition, are shown in dark gray and brown, respectively. Main chain atoms surrounding the residues of interest are colored in pale gray and in light red/brown for the E. faecalis acylhydrolase/lipase and AlgX structures, respectively. B, the bonds formed between the catalytic triad residues are shown in yellow. C, 10 residues of AlgX were independently mutated on the chromosome to alanine to probe their role in O-acetylation of alginate. These residues, depicted in stick representations and colored in yellow, were selected for mutation based upon their location within the putative active site. The residues found to be important for the acetylation of alginate are boxed.
