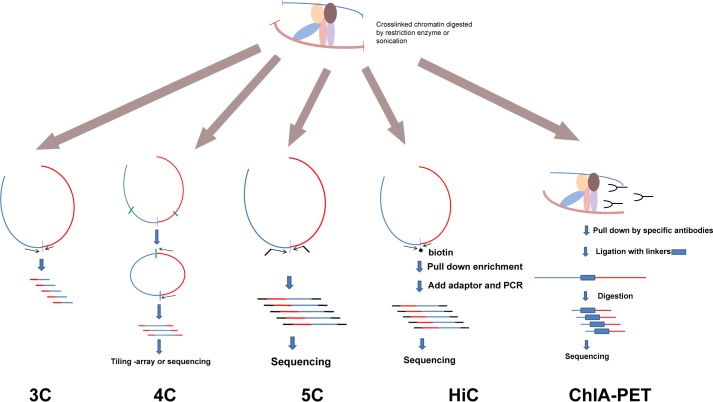
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of 3C-based methods. There are many methods derived from the original 3C design. Here, we present a few popular methods. In brief, cells are cross-linked, and chromatin is digested by restriction enzymes or sonicated. The structures of protein complexes containing DNA are preserved. These complexes are then diluted to a very low concentration, and ligation reactions are performed. Different amplification strategies are used to measure the relative cross-linking efficiency between loci. 3C is used to detect one specific interaction. 4C detects all possible interacting regions of one given locus. 5C and HiC provide “many-to-many” interacting efficiencies in a large genomic region or the whole genome. ChIP-PET includes immunoprecipitation to specifically examine the long-range interactions associated with a specific protein.