FIGURE 8.
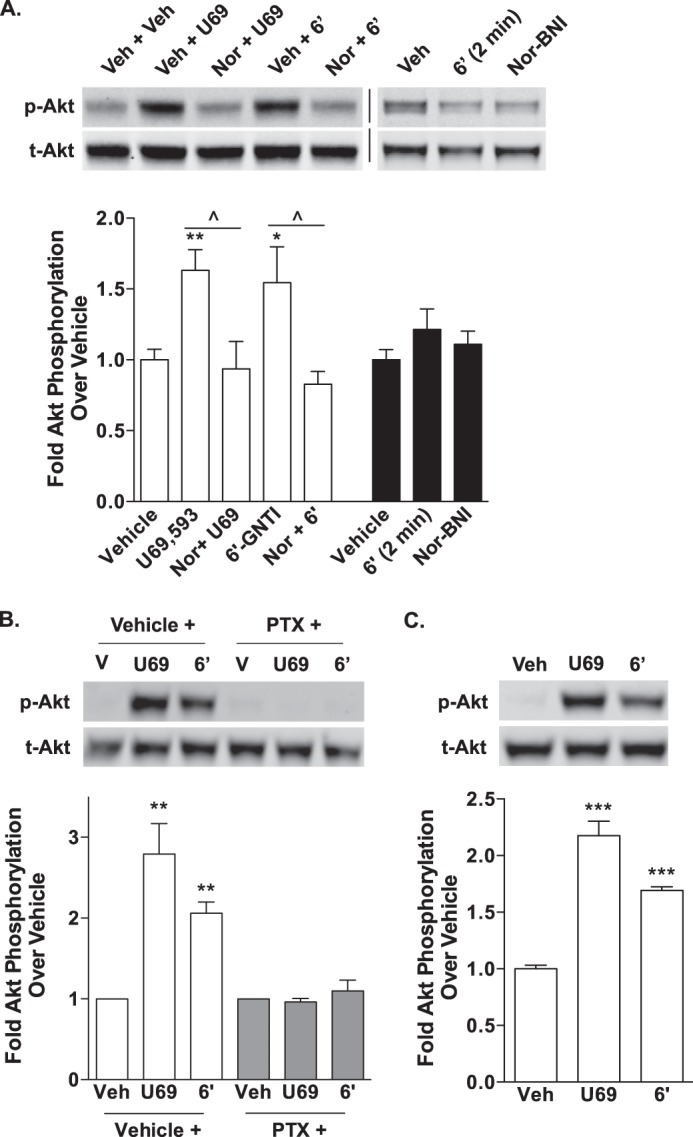
U69,593- and 6′-GNTI-mediated Akt phosphorylation in mouse primary striatal neurons is pertussis toxin-sensitive and β-arrestin2-independent. Primary striatal neurons were serum-starved for 1 h prior to the determination of Akt phosphorylation (10 μm for 10 min). Representative images of Western blots and densitometric analyses are provided. For each sample, phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) was first normalized to total Akt (t-Akt), and the -fold stimulation over vehicle is provided (mean ± S.E.). A, WT neurons were pretreated with either vehicle (Veh, 0.9% saline) or nor-BNI (Nor, 1 μm) during the last 15 min of the serum starvation. Akt is activated by both U69,593 (U69) and 6′-GNTI (6′) in a nor-BNI-sensitive manner (one-way ANOVA: for U69,593, F(2,13) = 8.247, p = 0.0049; for 6′-GNTI, F(2,14) = 5.662, p = 0.0158; Bonferroni's post hoc test: vehicle versus drug treatment groups, *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01; drug versus nor-BNI + drug, ^, p < 0.05; n = 5–6 independent neuronal preparations). Nor-BNI treatment alone does not alter Akt phosphorylation from vehicle levels (Student's t test: p > 0.05; n = 4 independent neuronal preparations). B, U69,593- and 6′-GNTI-induced Akt activation in WT striatal neurons is sensitive to overnight pretreatment with pertussis toxin (PTX; 100 ng/ml) (Student's t test: vehicle (V) versus drug treatment within each pretreatment group, **, p < 0.01; n = 3 independent neuronal preparations). C, U69,593 and 6′-GNTI induce an increase in Akt phosphorylation levels in striatal neurons cultured from βarr2-KO mice (Student's t test: ***, p < 0.001; n = 4 independent neuronal preparations).
