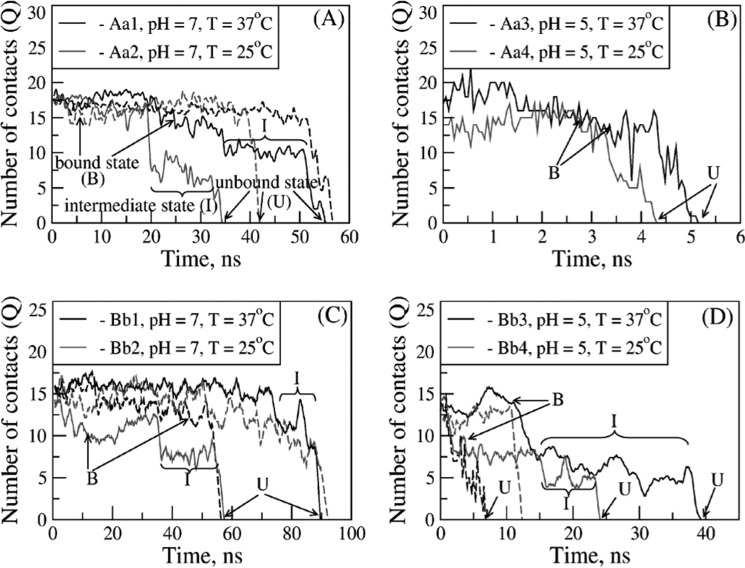
FIGURE 3.
Dependence of kinetic pathways for forced dissociation of the A:a and B:b knob-hole bonds on pH and temperature. Shown are the time-dependent profiles of the total number of binary contacts (Q) stabilizing the A:a knob-hole complex for model systems Aa1 and Aa2 (A) and Aa3 and Aa4 (B) and the B:b knob-hole complex for model systems Bb1 and Bb2 (C) and Bb3 and Bb4 (D). The profiles of Q indicate two distinct dissociation pathways: the one-step pathway of unbinding (B → U) from the bound state (B) to the unbound state (U) and the two-step pathway of unbinding (B → I → U) in which formation of the intermediate state (I) occurs. The time-dependent maps of binary contacts for A:a and B:b knob-hole bond complexes for different pH values and temperature are presented in supplemental Figs. S2 and S3, respectively.