FIGURE 5.
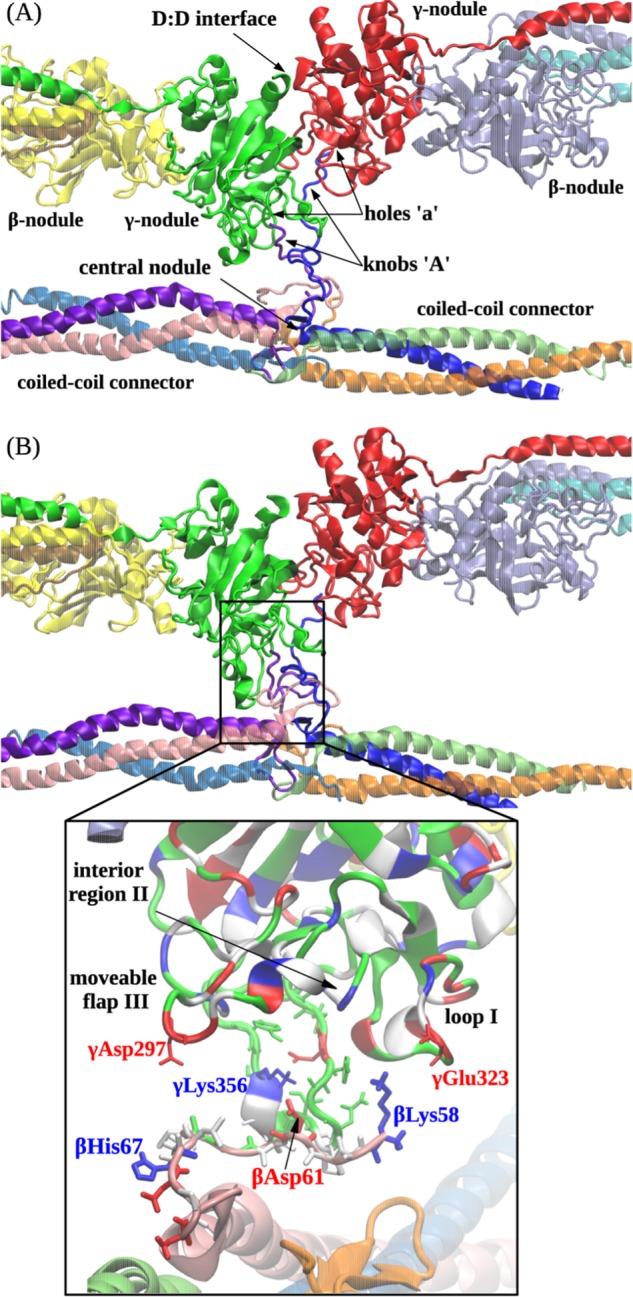
Computational reconstruction of the non-covalent coupling of the central nodule (bearing sites ‘A’) and the γ-nodules (bearing sites ‘a’). A, ribbon representation of the initial structure (before equilibration) of the double-D fragment of abutted fibrin molecules containing two γ- and two β-nodules. The residues in site ‘a’ form binding contacts with the residues of site ‘A’ emanating from the central nodule of the third fibrin monomer between the coiled coil connectors. B shows the translocation of the central nodule following formation of the A:a knob-hole bonds observed at the end of the simulation run. Also shown is the magnified view of electrostatic contacts between residues γGlu323 in loop I, γLys356 in the interior region, and γAsp297 in the moveable flap (all residues belong to site ‘a’ in the γ-nodule) and residues βLys58, βAsp61, and βHis67 in the N-terminal portion of the β chain in the central nodule (the GPR motif has been suppressed for clarity). In the central nodule, the residues colored in red represent negatively charged amino acids, whereas the residues colored in blue represent positively charged amino acids.
