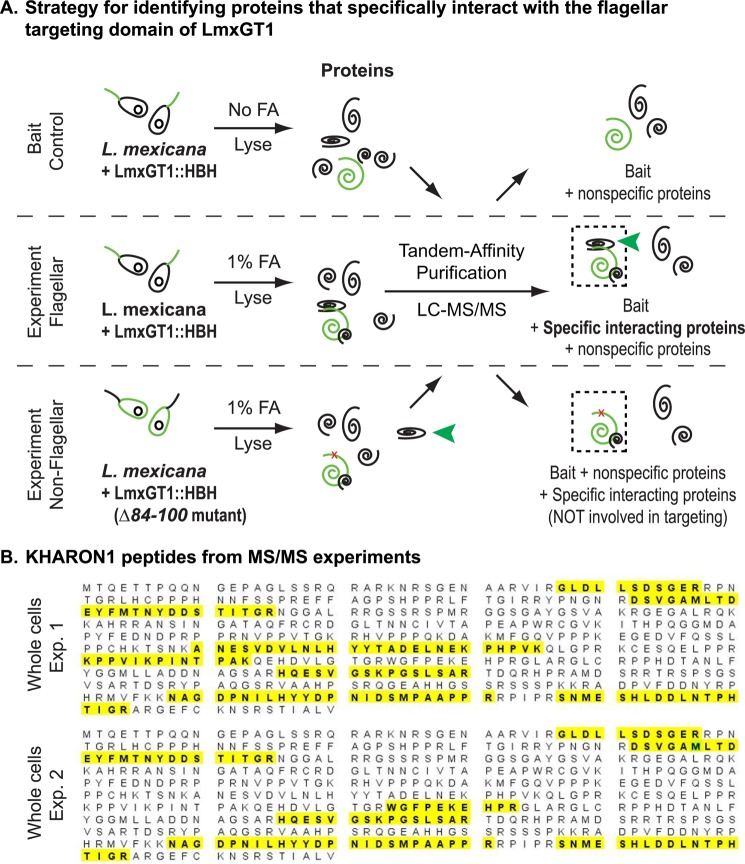
FIGURE 2.
Strategy for identifying proteins that specifically interact with the flagellar targeting domain of LmxGT1. A, three samples were analyzed: Bait Control in which parasites expressing LmxGT1::HBH were not cross-linked with formaldehyde (FA); Experiment Flagellar, in which LmxGT1::HBH expressing parasites were FA cross-linked; and Experiment Non-Flagellar, in which parasites expressing LmxGT1(Δ84–100)::HBH were FA cross-linked. Each sample was lysed and proteins that had been cross-linked to either wild type LmxGT1::HBH or LmxGT1(Δ84–100)::HBH were subjected to tandem affinity purification, and the TAP purified products were analyzed by tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). The green spiral represents LmxGT1::HBH, and the black spirals are proteins that are either specifically cross-linked or not cross-linked to LmxGT1::HBH. The dashed boxes indicate complexes of proteins that are cross-linked to LmxGT1::HBH and purified by TAP. The red x in LmxGT1::HBH in the bottom panel (Experiment Non-Flagellar) indicates the Δ84–100 deletion mutant that does not target to the flagellum. The green arrowhead indicates proteins that are specifically bound to the flagellar targeting domain of LmxGT1::HBH. Peptides identified from these three samples were compared to identify those that were present only in the Experiment Flagellar sample but not in the other two samples. B, peptides identifying KH1 from MS/MS spectra of the Experimental Flagellar sample are highlighted on the KH1 coding sequence.