FIGURE 4.
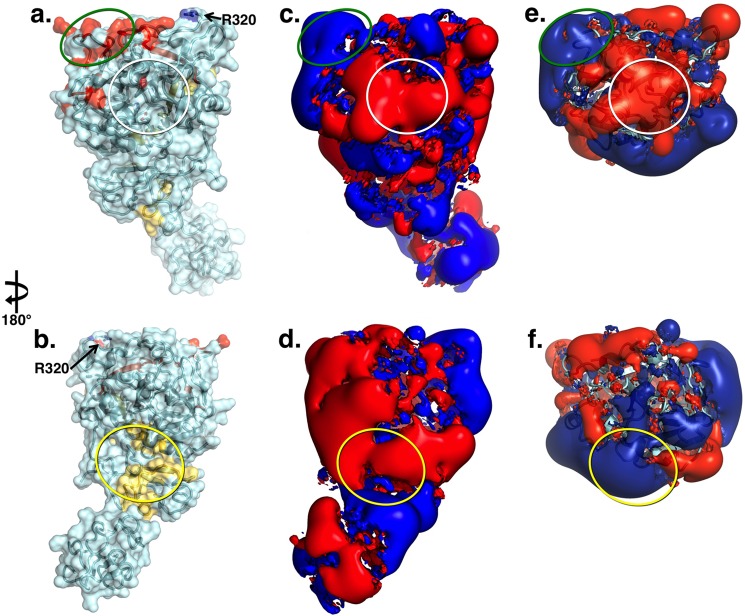
a and b, x-ray crystal structure of Gla-domainless prothrombin in surface/ribbon representation oriented with active site region (white circle) in the front (a) or rotated 180° (b) showing the bent conformation of the zymogen. Epitopes for factor Xa (yellow) and cofactor Va (red) identified by functional studies are mapped on the surface. The site of cleavage at Arg-271 is in a disordered region, but Arg-320 (Arg-15) is indicated. c and d, electrostatic potential surface of Gla-domainless prothrombin revealing the properties of the epitopes for factor Xa (yellow oval) and cofactor Va (green oval). The surface appears to be predominantly negative, especially in the region connecting kringle-2 to the protease domain housing the epitope for factor Xa binding. The epitope for cofactor Va recognition involves exosite I in the protease domain and is positively charged. The epitope for factor Xa on the C-terminal of the B chain is covered by the acidic residues connecting kringle-2 to the A chain and the junction between the two kringles. The electrostatic properties of this epitope change drastically upon cleavage at Arg-271 that generates prethrombin-2. e and f, cleavage at Arg-271 generates prethrombin-2 by removing the acidic linker between kringle-2 and the A chain and exposes the positively charged surface of exosite II on the protease domain. On the other hand, cleavage at Arg-271 has no effect on the epitope for cofactor Va recognition.