FIGURE 1.
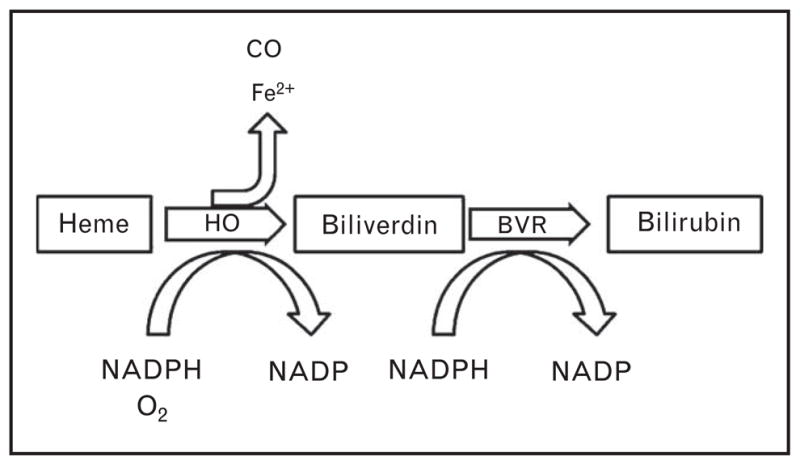
Degradation of heme-containing proteins leads to the release of free heme, a pro-oxidant molecule. In order to clear the potentially damaging molecule, heme oxygenase (HO) converts free heme to biliverdin, releasing free iron and carbon monoxide in the process. The biliverdin is then rapidly converted to bilirubin by biliverdin reductase (BVR). Biliverdin/bilirubin, elemental iron, and carbon monoxide all have important biological functions, making the activity of heme oxygenase an intriguing regulator of cellular and vascular function.
