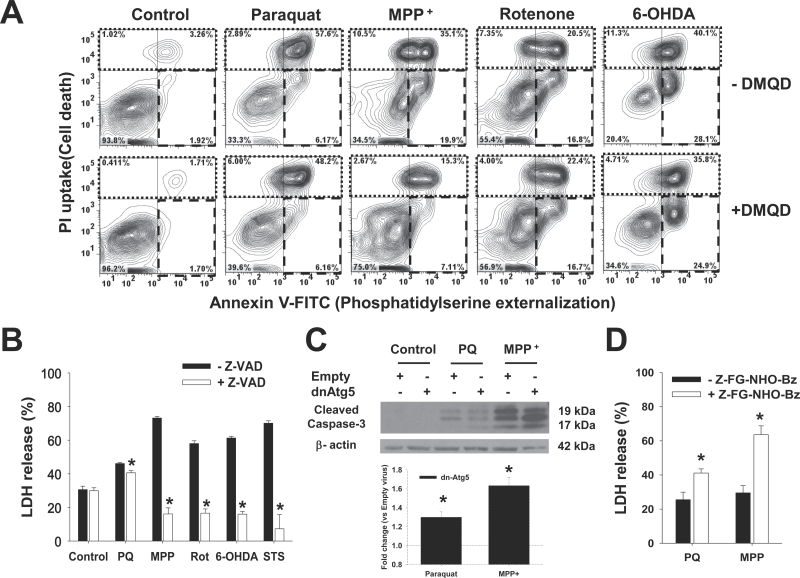
Fig. 6.
Caspases mediate cell death induced by the PQ, MPP+, rotenone, and 6-OHDA, whereas lysosomal hydrolase activity only regulates PQ and MPP+ toxicity. Cells were pretreated with the caspase-3 inhibitor Ac-DMQD-CHO (A), the pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK (B), or the cathepsin inhibitor Z-FG-NHO-Bz (D) at 50μM for 1h. In (C), cells were infected with Ad-Empty or Ad-dnAtg5 at 1.5 MOI for 24h. Then, cells were treated with PQ (0.5mM), MPP+ (2.5mM), rotenone (Rot, 4μM), 6-OHDA (50μM), or STS (20nM) for 48h. A, Apoptosis was measured by Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. In contour plots, early apoptosis is identified as an increase in the number of Annexin V (+)/PI (−) cells (lower right quadrant, broken line region). Late-apoptotic and necrotic cells are identified as Annexin V (+)/PI (+) (upper left quadrant, dotted line region). Plots are representative of 3 independent experiments. In (B and D), cell death was determined by measuring released LDH activity, and data represent percentage of released LDH and are means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. *p < .05, significant difference with respect to the corresponding neurotoxin treatments in the absence of caspase or cathepsin inhibitors. C, Representative WB analysis of caspase-3 activation. Inset bar graph represents the densitometric analysis of cleaved caspase-3/β-actin normalized with respect to the corresponding Empty virus + drug treatment values. Abbreviations: 6-OHDA, 6-hydroxydopamine; dnAtg5, dominant negative form of Atg5; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MOI, multiplicity of infection; MPP+ , 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium; PI, propidium iodide; PQ, paraquat; STS, staurosporine; WB, Western immunoblotting.