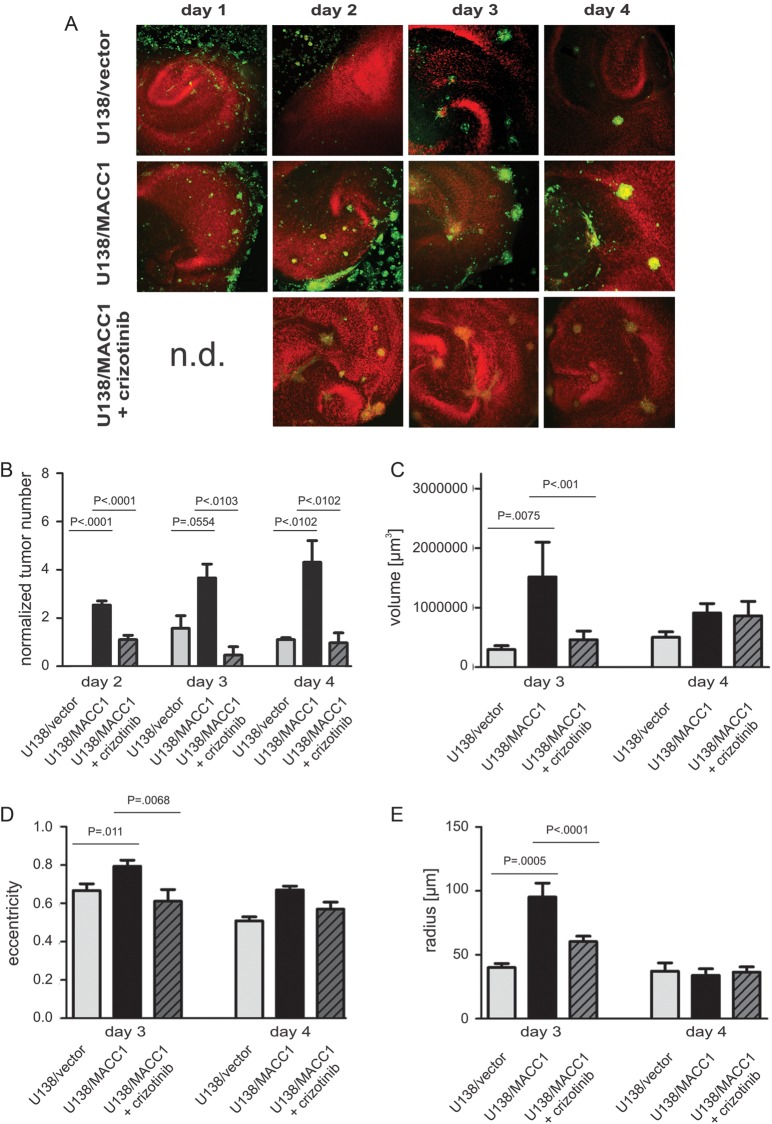
Fig. 4.
Tumor formation and morphological characterization of U138 cells in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures of mice with and without crizotinib. (A) Representative images of OHSC treated with U138/vector (upper panel), U138/MACC1 (middle panel), or U138/MACC1 + crizotinib (lower panel). Colonization of the OHSC by U138/MACC1 (middle panel) advanced in a shorter time period and by a higher number of tumor cells compared with U138/vector (upper panel) or cells treated with the c-Met inhibitor (lower panel). The cytoarchitecture was visualized by propidium iodide (red) and tumor cells were labeled by CFDA (green). (B) Quantification of the average tumor numbers per slide and 100 000 cells. (C) Quantification of averaged tumor volume in cubic micrometers with a minimal tumor diameter of 25 µm after 3 and 4 days. On day 3 a significant difference (P = .0075) was found between U138/MACC1 tumors and the vector control, which was reduced to basal levels by crizotinib. (D) Analysis of averaged eccentricities of U138/MACC1 and U138/vector tumors after 3 and 4 days in OHSC. After 3 days a significant difference between both cell types was observed (P = .011), which was prevented by the inhibitor. (E) Analysis of the mean radius of U138/MACC1 and U138/vector tumors after 3 and 4 days in OHSC. At day 3 a significant increase was observed for U138/MACC1 tumors vs vector controls (P = .0005), which was reverted by crizotinib. (B-E) Error bars: ± SEM; Abbreviation: n.d., not determined.