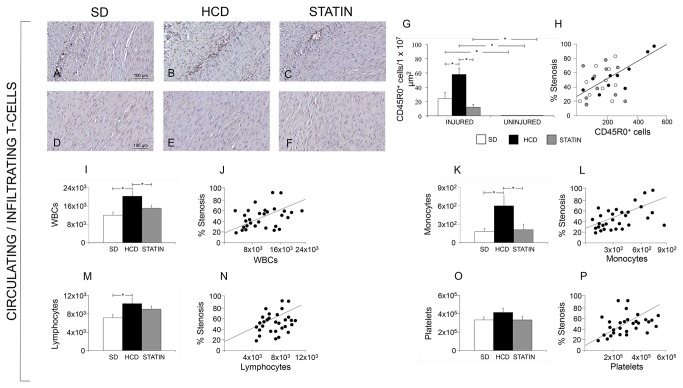
Figure 9. Atorvastatin significantly decreased circulating leukocytes and activated T-lymphocytes (CD45RO-positive) infiltrates in injured carotids.
The number of circulating WBCs, monocytes and lymphocytes was increased by hypercholesterolemia compared to SD pigs (20215 ±1934/mm3 vs. 11924±1388/mm3, p=0.05, panel I; 600±160/mm3 vs. 180±50/mm3, p=0.04, panel K; and 10200±1160/mm3 vs. 7120±700/mm3, p=0.05, panel M, respectively). This significant difference was abolished by atorvastatin treatment. There was a correlation between circulating WBCs, monocytes, lymphocytes, platelets and the degree of stenosis (r=0.454 p=0.04, J; r=0.710 p=0.01, L; r=0.484 p=0.03, N; r=0.487 p=0.03, P). The CD45RO-positive cell infiltrates in injured carotids was significantly increased in HCD pigs compared to SD ones (58±9 vs. 249± cells/1x107 μm2, p=0.05, panels A, B and G) while statin treatment reduced T-lymphocytes infiltration (12±4 vs. 58±9 cells/1x107 μm2, p=0.02, panels B, C and G). There were no CD45R0-positive cells in the contralateral uninjured carotid arteries (D-F). CD45R0-positive cells infiltration was positively correlated with the degree of stenosis (r=0.837, p=0.003, H).