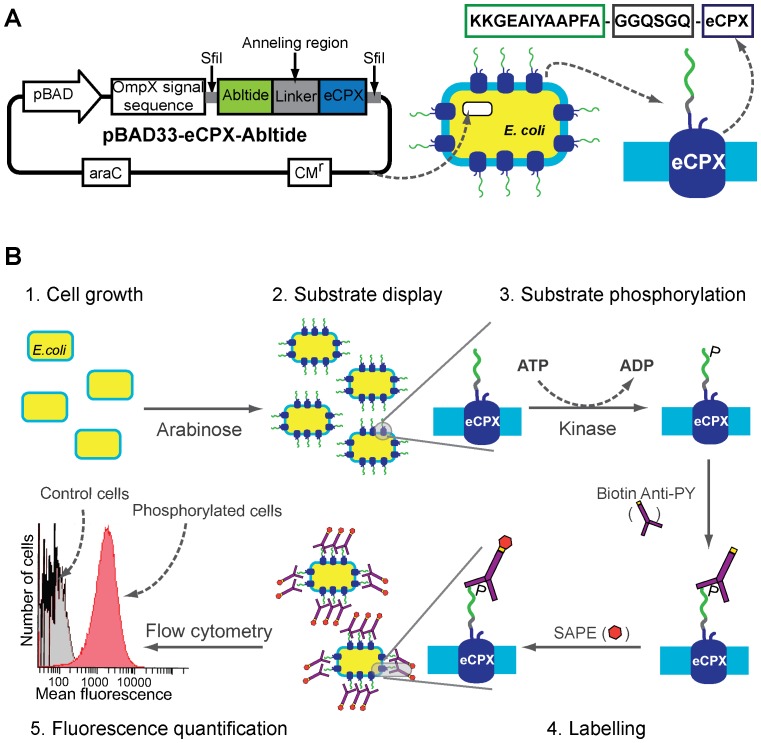
Figure 2. BacKin assay procedure.
(A) Map of plasmid pBAD33-eCPX-abltide (left) and schematic representation of abltide fused to eCPX expressed on the cell surface of an E. coli cell transformed with pBAD33-eCPX-abltide (right). The plasmid carries the arabinose promoter pBAD and resistance to chloramphenicol (CMr). The recognition sites for the restriction enzyme SfiI and annealing region are show. (B) Schematic representation of the BacKin assay: 1. E. coli cells transformed with eCPX-substrate plasmid are incubated at 37°C and shaken to grow until mid log phase; 2. Substrate (e.g. abltide) expression and display on the bacteria surface is induced with arabinose; 3. Substrate phosphorylation, cells are incubated with kinase (e.g. Abl kinase) and an excess of ATP; 4. Phosphorylated substrate is labeled by incubation of cells with biotinylated-anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (biotin-anti-PY) followed by incubation with streptavidin-phycoerythrin (SAPE); 5. Mean fluorescence of kinase-treated cells is quantified by flow cytometry and compared with mean fluorescence of kinase untreated cells.