Fig. 6.
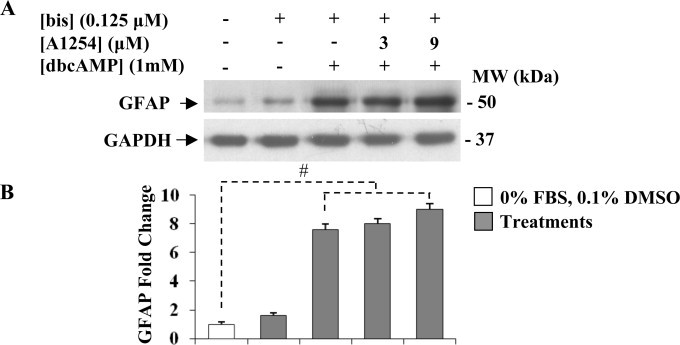
Effect of the protein kinase C inhibitor, bisindolylmaleimide (bis) on GFAP protein expression levels in dbcAMP-stimulated C6 cells exposed to A1254. Cells were treated with bis (0.125 μM) or co-exposed to bis (0.125 μM) and A1254 (3 or 9 μM) in presence of dbcAMP (1 mM) in serum-deprived medium containing 0.1% (v/v) DMSO, used as vehicle for A1254 and bis. After 24 h incubation, treated and untreated control cells were harvested and assayed for GFAP protein expression levels. Equal amounts of protein cell lysates (20 μg) were subjected to protein analysis by 12% SDS–PAGE. (A) Western blotting showing GFAP protein expression levels. GAPDH was used as loading control for cell lysates. Signals were revealed by immunostaining and ECL, as described in Section 2.5. (B) Densitometric analysis of GFAP protein expression levels. Fold change in GFAP protein levels was calculated by first normalizing to GAPDH levels in individual samples and then relative to untreated control cells cultured in serum-free DMEM with 0.1% (v/v) DMSO, (vehicle) set as 1. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM (n = 3). Columns with (#) were statistically different from untreated control cells or dbcAMP-differentiated cells (# p<0.001).
