Abstract
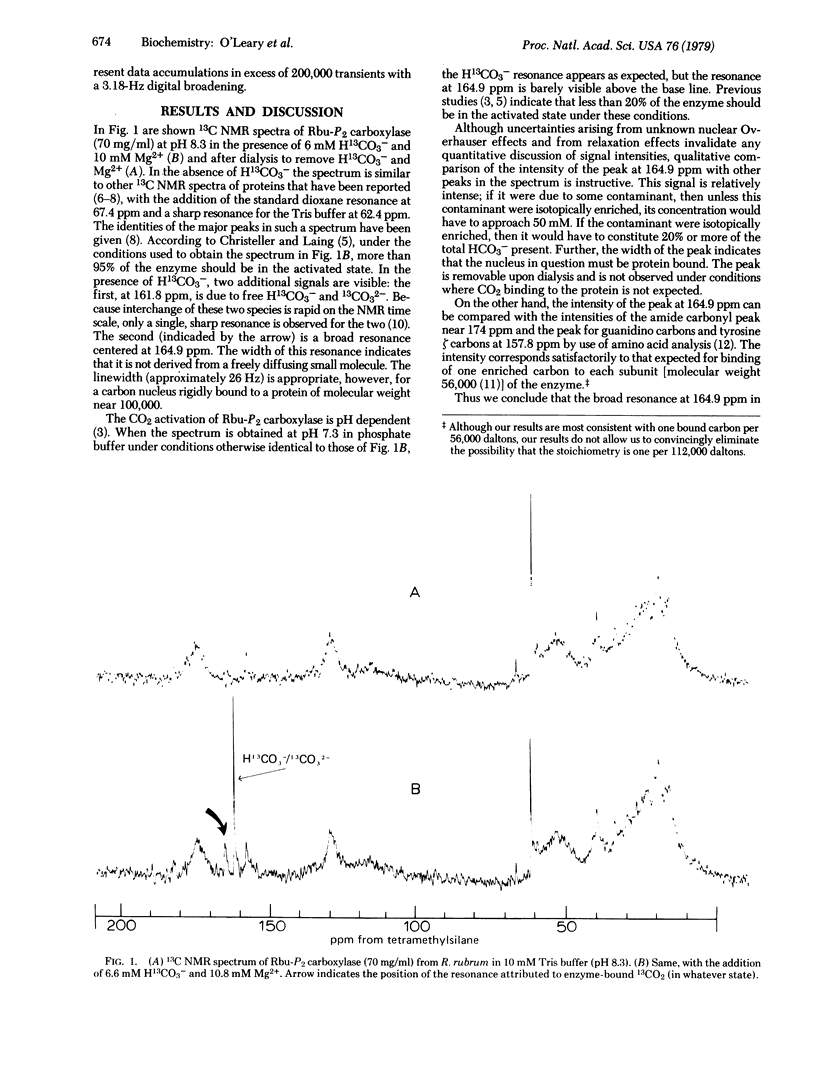
Ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase [3-phospho-D-glycerate carboxy-lyase (dimerizing), EC 4.1.1.39] from Rhodospirillum rubrum is activated by CO2 and Mg2+. 13C NMR spectra were determined for the unactivated enzyme and for enzyme that had been activated by 13CO2 and Mg2+. In addition to the expected resonance for H13CO3-/CO32- at 161.8 ppm downfield from tetramethylsilane, the spectrum of the activated enzyme shows a broad resonance at 164.9 ppm. Analogy with previous NMR studies of 13CO2 binding to hemoglobin [Morrow, J. S., Keim, P., Visscher, R. B., Marshall, R. C. & Gurd, F. R. N. (1973) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 70, 1414-1418], to myoglobin, and to amino acids [Morrow, J. S., Keim, P. & Gurd, F. R. N. (1974) J. Biol. Chem. 249, 7484-7494] suggests that the CO2 activation of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase involves formation of a carbamate between an enzyme amino group and CO2.
Keywords: photosynthesis, enzymology
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christeller J. T., Laing W. A. A kinetic study of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):467–473. doi: 10.1042/bj1730467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan W., Shindo H., Cohen J. S. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:383–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.002123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing W. A., Christeller J. T. A model for the kinetics of activation and catalysis of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):563–570. doi: 10.1042/bj1590563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. The activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by carbon dioxide and magnesium ions. Equilibria, kinetics, a suggested mechanism, and physiological implications. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):529–536. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. S., Keim P., Gurd F. R. CO2 adducts of certain amino acids, peptides, and sperm whale myoglobin studied by carbon 13 and proton nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7484–7494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. S., Keim P., Visscher R. B., Marshall R. C., Gurd F. R. Interaction of 13 CO 2 and bicarbonate with human hemoglobin preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1414–1418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton I. L., Welch M. H., Hartman F. C. Evidence for essential lysyl residues in ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase by use of the affinity label 3-bromo-1,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 1,4-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8062–8068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary M. H., Payne J. R. 13C NMR spectroscopy of labeled pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Model studies, D-serine dehydratase, and L-glutamate decarboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2248–2254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paech C., Ryan F. J., Tolbert N. E. Essential primary amino groups of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase indicated by reaction with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Feb;179(1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. V., Hartman F. C. Reaction of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase from rhodospirlilum rubrum with the potential affinity label 3-bromo-1,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 1,4-biphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 21;75(2):320–328. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. V., Stringer C. D., Hartman F. C. Identification of essential lysyl and cysteinyl residues in spinach ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase modified by the affinity label N-bromoacetylethanolamine phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5707–5711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. I. Levels, purification, and effects of metallic ions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3453–3458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman W. B., Tabita F. R. Modification of Rhodospirillum rubrum ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase with pyridoxal phosphate. 1. Identification of a lysyl residue at the active site. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1282–1287. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


