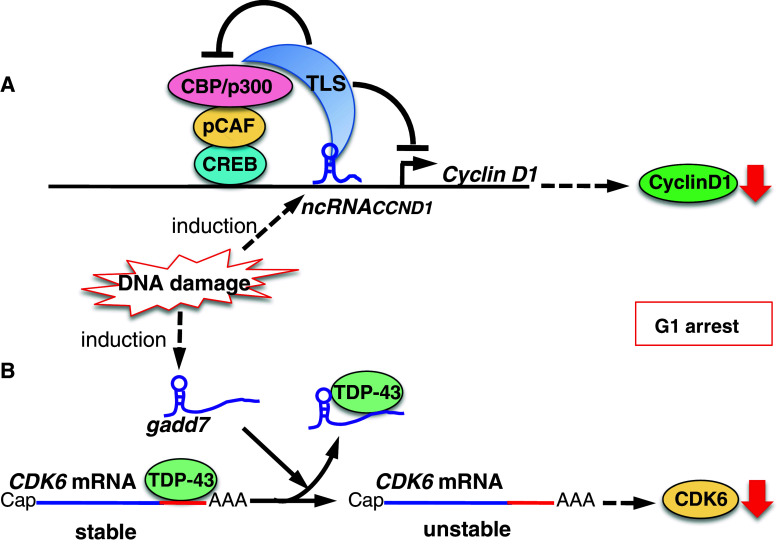
Fig. 2.
Model showing the proposed mechanisms of lncRNA-mediated regulation of cyclin D1 (a) and CDK6 (b) induced by DNA damage. a DNA damage induces the transcription of ncRNA CCND1 from the promoter region of the cyclin D1 gene. ncRNA CCND1 associates with and recruits TLS, an RNA binding protein, to the cyclin D1 promoter. The ncRNA CCND1–TLS complex inhibits the CBP/p300–pCAF–CREB coactivator complex and thereby prevents cyclin D1 gene transcription. b DNA damage induces the expression of the lncRNA, gadd7, which dissociates TDP-43 from the CDK6 mRNA to destabilize it, and CDK6 is thereby downregulated, inhibiting the G1/S transition. The lncRNAs gadd7 and ncRNA CCND1 may collaboratively participate in the G1 checkpoint in response to DNA damage