Figure 3.
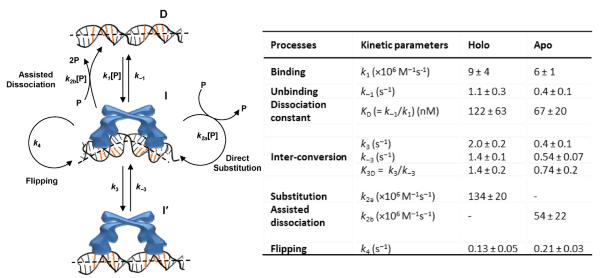
Left: kinetic mechanism of CueR interactions with a specific DNA, which includes the protein (P), DNA (D), two protein–DNA complexes that differ in protein binding modes (I and I′ ), and the rate constants for the kinetic processes. [P]: protein concentration. Between k2a and k2b, the direct substitution process k2a is dominant for holo-CueR–DNA interactions, whereas the assisted dissociation process k2b is dominant for apo-CueR–DNA interactions. Right: the kinetic parameters. The rate constants for CueR (holo) binding and unbinding with nonspecific DNA are k1 = 0.016 ± 0.001 nM−1 s−1 and k−1 = 5.9 ± 0.1 s−1; other kinetic processes do not occur to nonspecific DNA (35).
