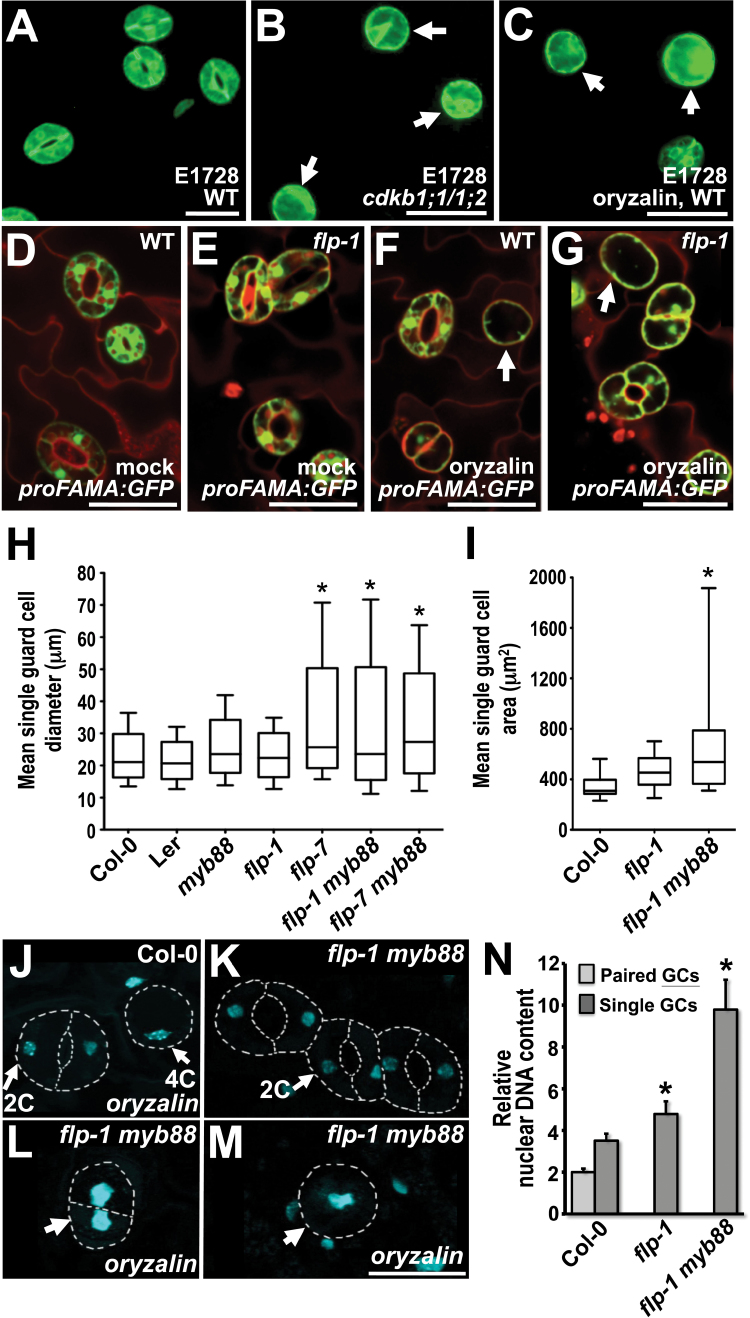
Fig. 1.
Chemical disruption of mitosis induces enlarged and highly endoreplicated single guard cells (sGCs) in flp myb88 mutants. (A) Wild-type stomata expressing the mature guard cell fate marker, E1728. (B) cdkb1;1 cdkb1;2 sGCs expressing E1728 (arrows). (C) Oryzalin-induced sGCs in wild-type also express E1728. (D–G) proFAMA:GFP expression which also marks GC fate. (D) Wild-type control (DMSO treatment). (E) flp-1 mutant background (DMSO). (F) Wild-type stomata treated with oryzalin for 24h showing an undivided sGC (arrow). (G) flp-1 treated with oryzalin showing a sGC (arrow). (H) Mean GC diameter 6 d after treatment with 25 µM oryzalin for 24h as a function of genotype. The diameters of normal GCs as well as abnormal sGCs were scored. Genotypes ranked from lowest to highest diameters (bars). (I) Mean GC area after oryzalin treatment. Three-day-old Col-0, flp-1, and flp1 myb88 seedlings treated and scored as in (H). Genotypes ranked from lowest to highest values (bars). Data in (H) and (I) presented as box plots, in which the box encompasses data for the 25th to 75th percentiles. The horizontal line within each box is the median (50%). Error bars represent the 5th (lower bar) and the 95th (upper bar) percentiles. (A–G) Scale bars=25 µm. Stars (*) denote means significantly different from the wild type (P <0.005). (J–N) Cotyledons from Col-0, flp-1, and flp-1 myb88 plants were treated with oryzalin (or DMSO control) for 24h after staining with 4′6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Nuclear fluorescence was imaged using wide-field microscopy. Whereas sGCs that form after oryzalin treatment display mostly 4C levels in wild-type plants, in flp1 myb88 this mean was 10C. (J–M) Micrographs showing examples of normal and enlarged guard cell nuclei. Stomatal outlines indicated by dashed lines. Arrows indicate nuclei in guard cells that are enlarged compared with other nuclei shown and that probably contain 4C DNA levels. (J–M) Bars=25 µm. (J) Stomata from wild-type (Col-0) plants treated with oryzalin. Left: probably 2C guard cells in a normal stoma. Right: a sGC with a larger nucleus likely to be 4C. (K) Stomatal cluster in a flp-1 myb88 cotyledon that was not treated with oryzalin containing 2C DNA levels in guard cells. (L, M), flp-1 myb88 cotyledons treated with oryzalin. Arrows indicate enlarged nuclei. (L) Nuclei are enlarged in both GC-like cells. (M) Enlarged nucleus in sGC. Stomatal morphogenesis appears to be blocked or delayed. (N) Graph showing nuclear sizes in Col-0, flp-1, and flp-1 myb88 plants treated with oryzalin. Relative DNA levels quantified by the areas of nuclei/gray values derived from DAPI-fluorescence. Only single guard cells were sampled in flp-1 and flp-1 myb88. Sample sizes: Col-0: 145 paired GCs and 65 sGCs; flp-1: 59 sGCs; 48 flp-1 myb88 sGCs. Bars, means ±SE. Stars (*) denote means significantly different from the wild type (P <0.001). (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)