Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the molecular pathways of the regulation of actin cytoskeleton remodeling through the interaction of activated RhoGTPases with effector proteins.
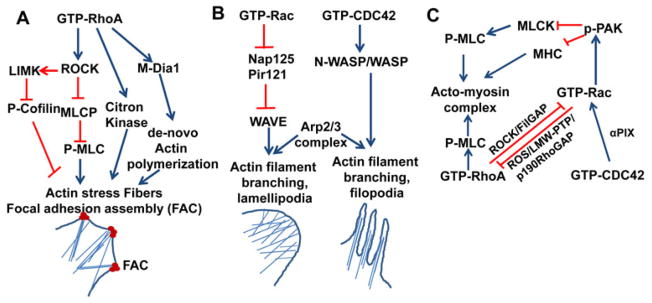
(A). Activated RhoA through effector protein ROCK phosphorylates and inhibits myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCK) activity that leads to the elevation of p-MLC level inside the cells. ROCK phosphorylates and activates LIM kinase (LIMK). LIMK in turn phosphorylates and inactivates cofilin. Increased levels of p-MLC and p-cofilin favor actin stress fiber formation. RhoA activated ROCK phosphorylates and activates citron kinase. Activated citron kinase phosphorylates MLC and increased the bundling of actin filaments at the cleavage furrow during cytokinesis. GTP coupled RhoA interacts and activates the auto inhibited formin or mDia1 that induces the de novo actin polymerization at the barbed end of F-actin. (B). Activated Rac and Cdc42 activate WAVE and WASP, respectively. Activated WAVE and WASP through their interaction with Arp2/3 complex initiate’s actin polymerization on the side of existing actin filament producing branched actin network that induces the formation of lamellipodia and filopodia at the leading edge of migrating cells. (C). Cross talk between Rho GTPases. Cdc42 through its interaction with α-PIX cooperates with Rac at the leading edge. Activated Rac induces ROS generation and ROS inhibits LMW-PTP, and thereby upregulates p190RhoGAP activity that in turn inhibits RhoA. Activated Rac through its effector p21-activated protein kinase (PAK) inhibits MLCK that results in decreased pMLC level. PAK phosphorylates and inactivates MHC. The combined effect of the reduction of pMLC level and phosphorylation of MHC negatively regulates the actin stress fiber formation. Rho/ROCK mediated activation of FilGAP inhibits Rac activity, as FilGAP has Rac specific GAP functional GAP domain. FAC, focal adhesion complex; ROCK, Rho Kinase; p-MLC, phosphorylated myosin light chain; MHC, myosin heavy chain; mDia1, Drosophila homologue of mammalian diaphanous related protein, α-PIX, PAK interacting exchange factor. Blue arrows denote activation pathways. Red blunt lines denote inhibitory pathways.
