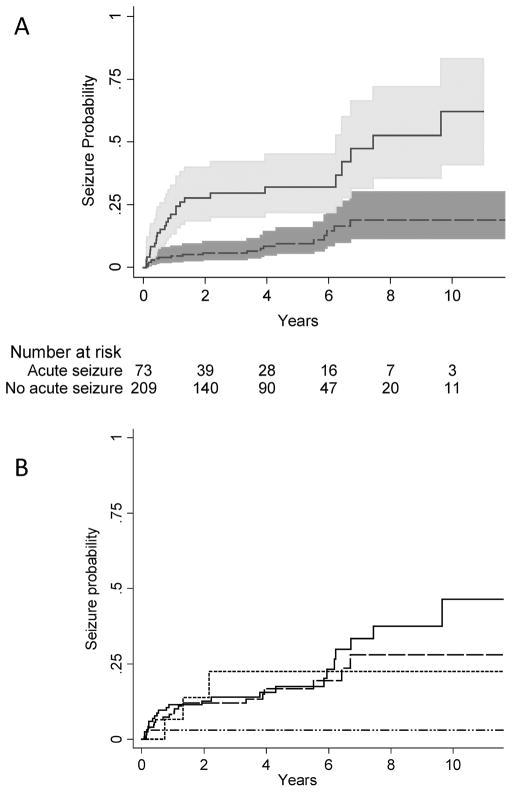
Figure 2.
Among children with stroke enrolled in Kaiser Permanente Northern California, 1993–2007, Kaplan-Meier plots demonstrating (A) a four-fold (HR 4.1, 95% CI 2.3, 7.3) increased risk of remote seizure among children with acute seizures (solid line, 95% confidence interval in light gray shading) compared to children without acute seizures (dashed line, 95% confidence interval in dark gray shading); and (B) the cumulative incidence of remote seizure stratified by stroke type: arterial ischemic stroke (solid line), intraparenchymal hemorrhage (large dashes), venous sinus thrombosis (small dashes) SAH/IVH (dash and dots). The x-axis is time from 30 days post-stroke.