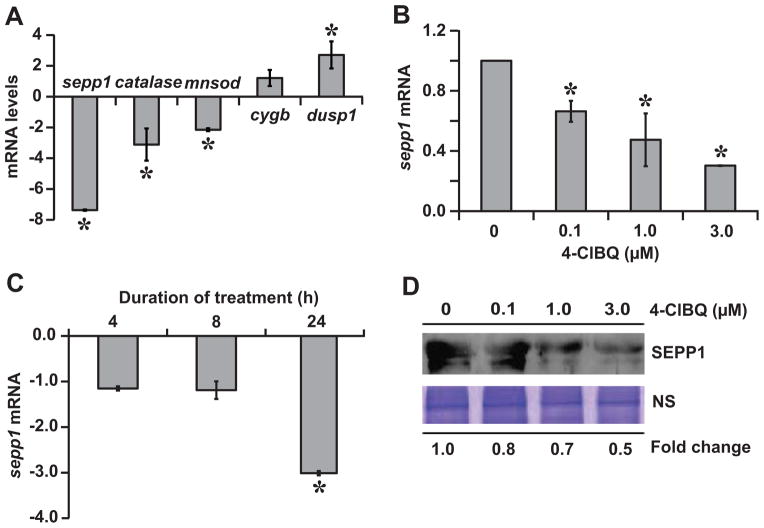
Fig. 4.
4-ClBQ treatment significantly inhibits sepp1 expression. (A) mRNA levels of sepp1, catalase, mnsod, cygb, and dusp1 that showed significant changes in the PCR-array were further verified by performing a quantitative RT-PCR assay; fold-change was calculated relative to individual mRNA levels in untreated cells. Quantitative RT-PCR measurements of sepp1 mRNA levels in (B) 24 h 4-ClBQ (0–3.0 μM) treated cells, and (C) 3.0 μM 4-ClBQ treated cells at the end of 4, 8, and 24 h of treatments. Fold change was calculated relative to time-matched untreated cells. Asterisks represent statistical significance compared to untreated cells; P < 0.05, n = 3. (D) Total proteins were precipitated from media collected from control and 4-ClBQ treated cells. SEPP1 protein levels were analyzed by immunoblotting. A Coomassie blue stained polypeptide band was used for loading correction.