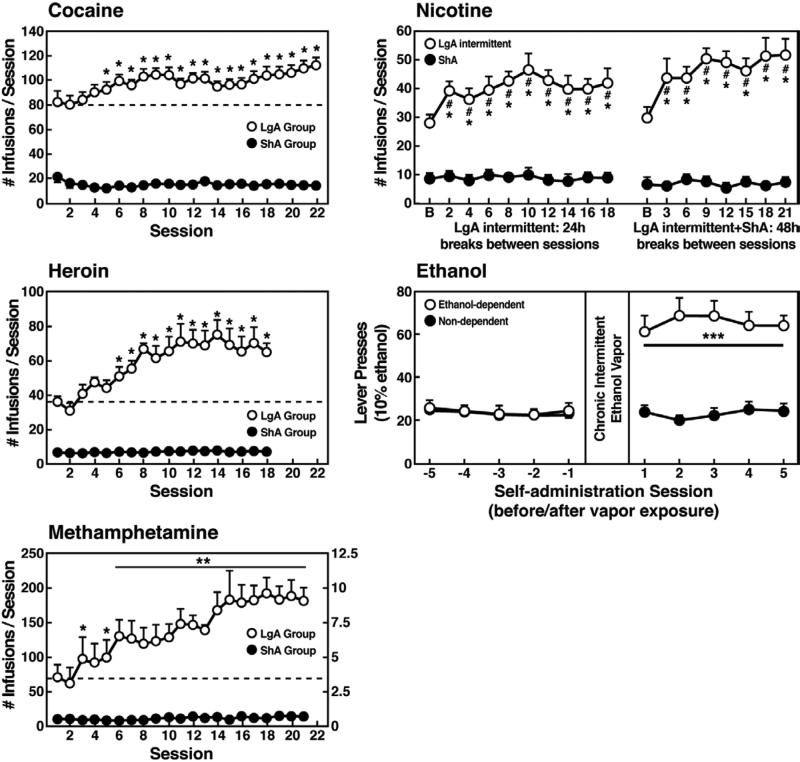
Figure 1.
(A) Effect of drug availability on cocaine intake (mean ± SEM). In long-access (LgA) rats (n = 12) but not short-access (ShA) rats (n = 12), the mean total cocaine intake started to increase significantly from session 5 (p < 0.05; sessions 5 to 22 compared with session 1) and continued to increase thereafter (p < 0.05; session 5 compared with sessions 8-10, 12, 13, and 17-22). [Taken with permission from Ahmed and Koob, 1998.] (B) Effect of drug availability on total intravenous heroin self-infusions (mean ± SEM). During the escalation phase, rats had access to heroin (40 μg per infusion) for 1 h (ShA rats, n = 5-6) or 11 h per session (LgA rats, n = 5-6). Regular 1-h (ShA rats) or 11-h (LgA rats) sessions of heroin self-administration were performed 6 days a week. The dotted line indicates the mean ± SEM number of heroin self-infusions in LgA rats during the first 11-h session. *p < 0.05, different from the first session (paired t-test). [Taken with permission from Ahmed et al., 2000.] (C) Effect of extended access to intravenous methamphetamine on self-administration as a function of daily sessions in rats trained to self-administer 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 mg/kg/infusion of intravenous methamphetamine during the 6-h session. ShA, 1-h session (each unit dose, n = 6). LgA, 6-h session (0.05 mg/kg/infusion, n = 4; 0.1 mg/kg/infusion, n = 6; 0.2 mg/kg/infusion, n = 5). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, compared with day 1. [Taken with permission from Kitamura et al., 2006.] (D) Nicotine intake (mean ± SEM) in rats that self-administered nicotine under a fixed-ratio (FR) 1 schedule in either 21 h (long access [LgA]) or 1 h (short access [ShA]) sessions. LgA rats increased their nicotine intake on an intermittent schedule with 24-48 h breaks between sessions, whereas LgA rats on a daily schedule did not. The left shows the total number of nicotine infusions per session when the intermittent schedule included 24 h breaks between sessions. The right shows the total number of nicotine infusions per session when the intermittent schedule included 48 h breaks between sessions. #p < 0.05, compared with baseline; *p < 0.05, compared with daily self-administration group. n = 10 per group. [Taken with permission from Cohen et al., 2012.] (E) Ethanol self-administration in ethanol-dependent and nondependent animals. The induction of ethanol dependence and correlation of limited ethanol self-administration before and excessive drinking after dependence induction following chronic intermittent ethanol vapor exposure is shown. ***p < 0.001, significant group × test session interaction. With all drugs, escalation is defined as a significant increase in drug intake within-subjects in extended-access groups, with no significant changes within-subjects in limited-access groups. [Taken with permission from Edwards et al., 2011.]