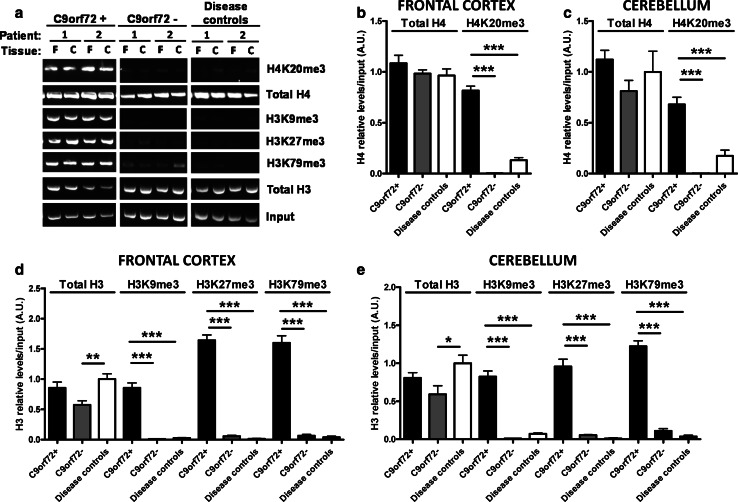
Fig. 2.
Reduced C9orf72 mRNA expression levels in the C9orf72+ group result from aberrant binding to trimethylated histone residues. a Electrophoretic representation of chromatin immunoprecipitated DNA in a subgroup of participants tested. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was performed on two different human tissues, frontal cortex (F) and cerebellum (C), using antibodies specific for total histones H3 and H4 or trimethylated histones H3K9, H3K27, H3K79, and H4K20. Following pull-down, bound DNA was purified and used for PCR amplification of the C9orf72 promoter region. This region was successfully amplified in the C9orf72+ group when ChIP was carried out with antibodies targeting trimethylated histone residues; under the same conditions, this region was not amplified in C9orf72− and disease controls, indicating an absence of binding. The complete figure is provided in the online resource. b, c, d, e Relative quantifications of all brain DNA were performed by measuring band intensity (complete gels in the online resource, Fig. 2) for each immunoprecipitated histone and presented as a ratio to the input. Each graph is normalized to total histone levels in the disease control group (mean value set to 1). Statistical differences were calculated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005. A clinical description of participants is available in Table 2 (online resource)