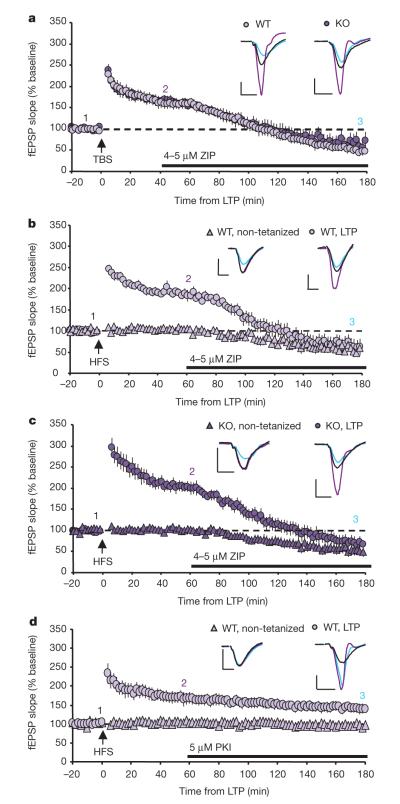
Figure 3. ZIP is not specific for PKM-ζ.
a, ZIP is equally effective at reversing established TBS-LTP in WT mice and mice lacking PKM-ζ. Before ZIP application (40 min post-LTP): WT, n=8, 166±12%; KO, n=6, 167±10%, P>0.9. 140 min after ZIP application: WT, 48±7%; KO, 60±18%, P>0.5. b, c, ZIP decreases both tetanized (HFS) and non-tetanized synaptic responses in WT mice (b) and mice lacking PKM-ζ (c). Before ZIP application (60 min post-LTP): WT, n=8, tetanized=181±8%, non-tetanized=102±4%; KO, n=8, tetanized=203±12%, non-tetanized=100±4%, P>0.15 WT vs KO tetanized or non-tetanized. 120 min after ZIP application: WT, tetanized=60±18%, non-tetanized=50±9%; KO, tetanized=67±14%, non-tetanized=52±11%, P>0.6 WT vs KO tetanized or non-tetanized. d, Myristoylated PKI peptide does not affect LTP or basal transmission (tetanized n=5, non-tetanized n=4). Data represent mean±s.e.m. Scale bars, 0.5 mV (vertical), 5 ms (horizontal).