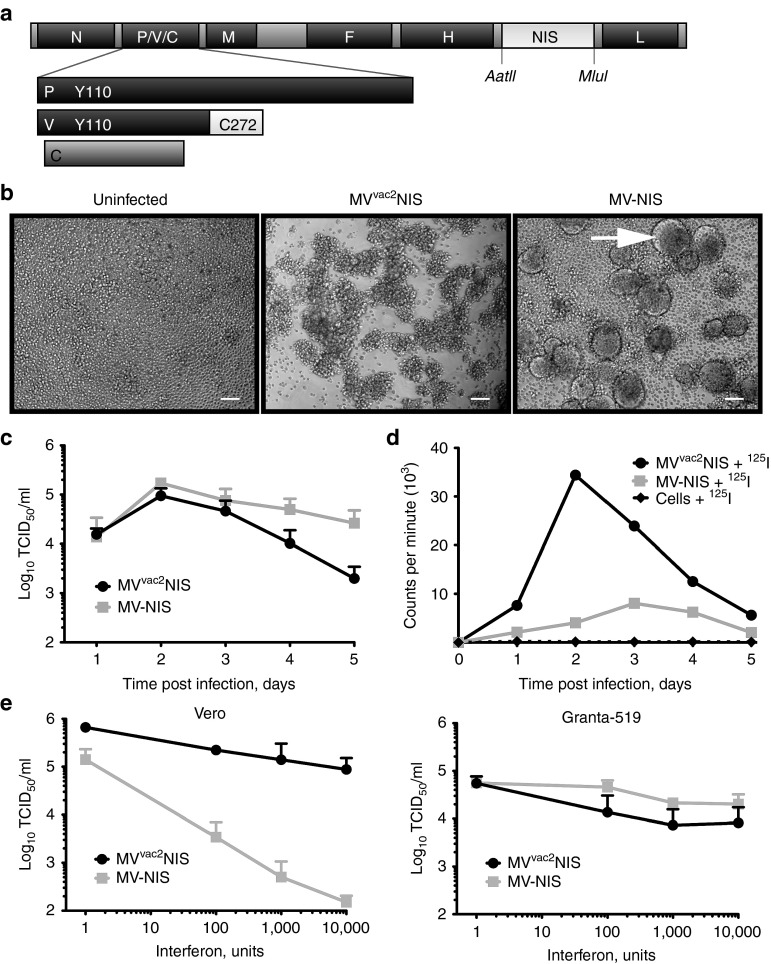
Figure 1.
MVvac2NIS efficiently expresses functional NIS within infected MCL cells, and can overcome interferon signaling. (a) Map of the p(+)MVvac2NIS plasmid coding for the MVvac2NIS genome. The human NIS gene was inserted in an additional transcription unit downstream of MV-H. The AatII and MluI restriction sites are indicated. Residues in the P and V proteins important for antagonizing cellular interferon responses are indicated. (b) Light microscopy images of Granta-519 cells, uninfected (left) or infected with MVvac2NIS (center) or MV-NIS (right) at 48 hours after infection at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.03. Scale bars = 5 µm. (c) Virus titer for MVvac2NIS and MV-NIS recovered from cell-associated fraction following Granta-519 infection at an MOI of 0.03. Data are given as mean ± SD; n = 3. (d) Intracellular uptake of 125I by Granta-519 cells infected or not with MVvac2NIS or MV-NIS at an MOI of 0.03. Representative experiment. (e) Quantification of virus titer after MVvac2NIS or MV-NIS infections in the presence of increasing concentrations of human leukocyte interferon in Vero (left, 24 hours after infection) and Granta-519 (right, 48 hours after infection) cells. Data are given as mean ± SD; n = 3. MCL, mantle cell lymphoma; MV, measles virus.