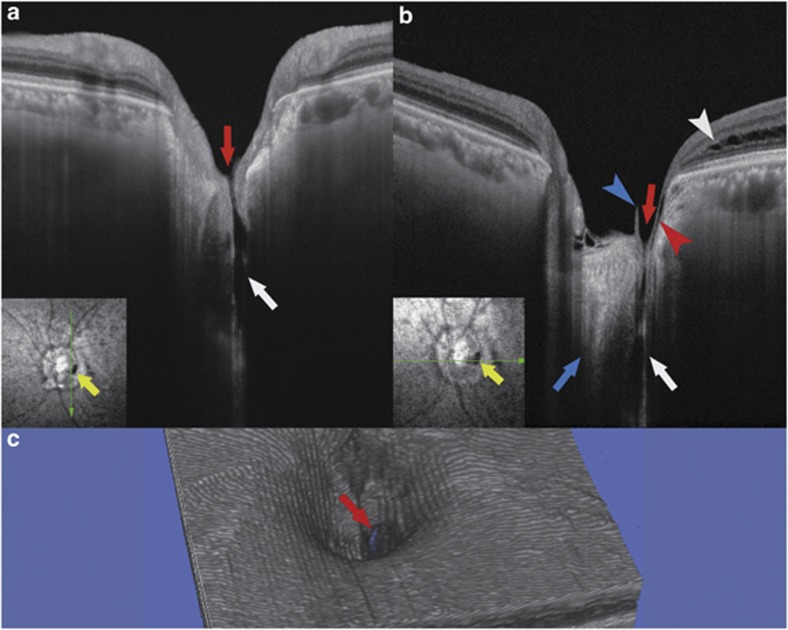
Figure 2.
Swept-source optical coherence tomographic (SS-OCT) image of the left eye with an optic disc pit. The imaging depth of this SS-OCT system is 2.6 mm in tissue. (a, b) Vertical (a) and horizontal (b) B-scan cross-sectional images near the optic disc pit are shown. Retrobulbar subarachnoid space (white arrows) is clearly seen around the optic nerve. There is a direct communication between the retrobulbar subarachnoid space and the vitreous cavity (red arrows). Blue arrow indicates the optic nerve. Red arrowhead indicates a thin line of fluid that is presumably connecting with the retrobulbar subarachnoid space, but communication with this line and the schisis cavity (white arrowhead) is unclear. Blue arrowhead points to a part of a vitreous strand. Yellow arrows indicate the optic disc pit, and green arrows indicate the direction of the OCT scan. (c) Three-dimensional OCT reconstruction shows a break in the cup of the optic disc (red arrow).