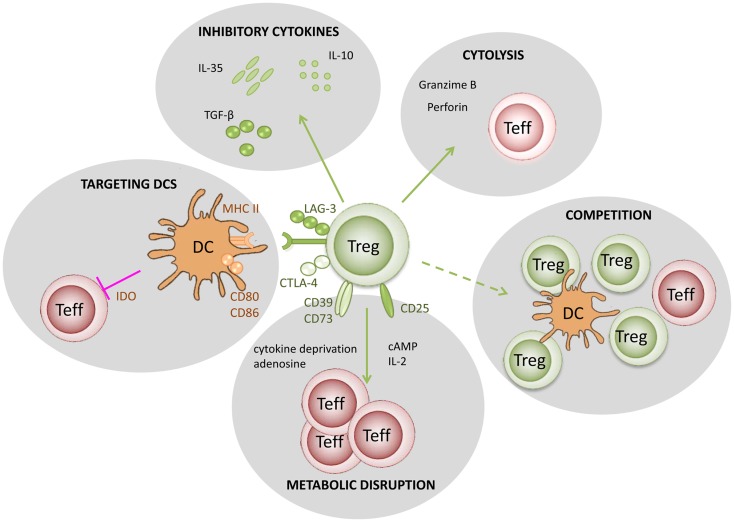
Figure 1.
Putative mechanisms used by regulatory T cells. (1) Targeting DCs – modulation of antigen-presenting cell activity through Treg engagement of co-stimulatory receptors on the DC surface, leading to weak or abrogated signals to naïve/effector T cells; (2) Metabolic disruption – includes cytokine deprivation, cyclic AMP-mediated inhibition, and adenosine receptor (A2A)-mediated immunosuppression; (3) Competition – for critical cytokines, such as IL-2, or direct disruption of effector cell engagement with APCs; (4) Cytolysis – direct cytotoxic effect through the production of Granzyme B and Perforin and consequent apoptosis of effector T cells or APCs; (5) Production of inhibitory cytokines – including IL-10, IL-35, and TGF-β.