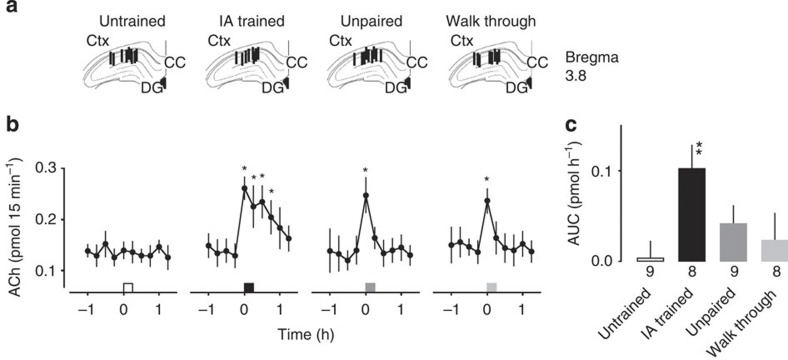
Figure 2. ACh levels in the rat hippocampal CA1 region under different learning conditions.
(a) Locations of the in vivo microdialysis probe in the hippocampal CA1 region. Vertical lines represent the 0.5-mm length of the dialysis membrane. CC, corpus callosum; DG, dentate gyrus. Ctx: cortex. (b) Extracellular ACh levels increased significantly during inhibitory avoidance (IA) learning, and remained high for 60 min. In the unpaired or walk-through control animals, the ACh level increased but only transiently. Squares indicate the timing of the behavioural task. (c) ACh AUC during and after behavioural tests. The number of rats in each group is shown at the bottom of each bar. *P<0.05 versus pretraining level. One-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis with the Fisher’s protected least significant difference (PLSD) test. **P=0.0019 versus untrained, 0.048 versus unpaired and 0.018 versus walk through. One-way factorial ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis with the Fisher’s PLSD test. Untrained: n=9, IA trained: n=8, unpaired: n=9, walk through: n=8, error bars indicate± s.e.m.