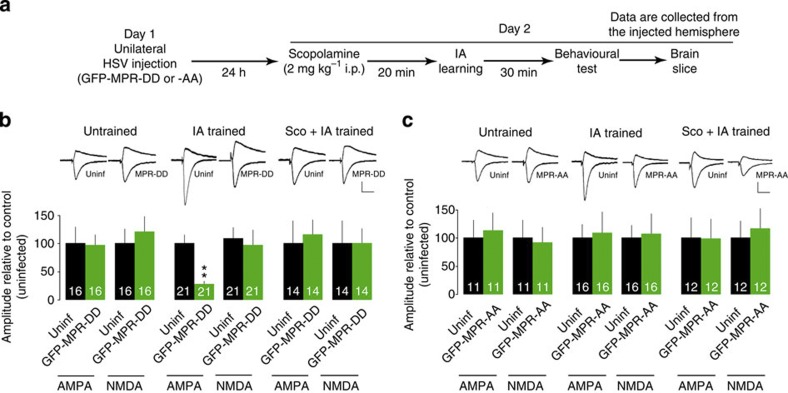
Figure 4. mAChRs mediate learning-dependent synaptic delivery of endogenous GluA1-containing AMPARs.
(a) Experimental design of unilateral gene delivery (GFP-MPR-DD or -AA) and the inhibitory avoidance (IA) task. Data are collected from the injected hemisphere. (b) Unilateral GFP-MPR-DD expression attenuated the learning-dependent synaptic delivery of endogenous GluA1-containing AMPARs in CA1 pyramidal neurons, and scopolamine (Sco) pretreatment with systemic injection blocked this effect. Synaptic transmission from CA3 to CA1 pyramidal neurons was recorded simultaneously from neurons infected with viruses expressing GFP-MPR-DD and nearby uninfected (uninf.) neurons. GFP-MPR-DD expression prevented the potentiation of AMPA transmission in IA-trained rats (**P=0.001 versus uninfected, n=21; the Wilcoxon test), but had no effect in untrained (P=0.72, n=16; the Wilcoxon test) or IA-trained rats in the presence of Sco (P=0.30, n=14; the Wilcoxon test). NMDA transmission was unchanged by GFP-MPR-DD expression in these groups. (c) Unilateral GFP-MPR-AA expression did not affect synaptic transmission in any group. For graphic display, the amplitudes of the corresponding uninfected neurons were designated as 100%. Representative traces are shown in top insets. The number of pairs in each group is shown at the bottom of each bar. Error bars indicate ±s.e.m. Vertical scale bars, 40 pA; horizontal scale bars, 50 ms.