Figure 2.
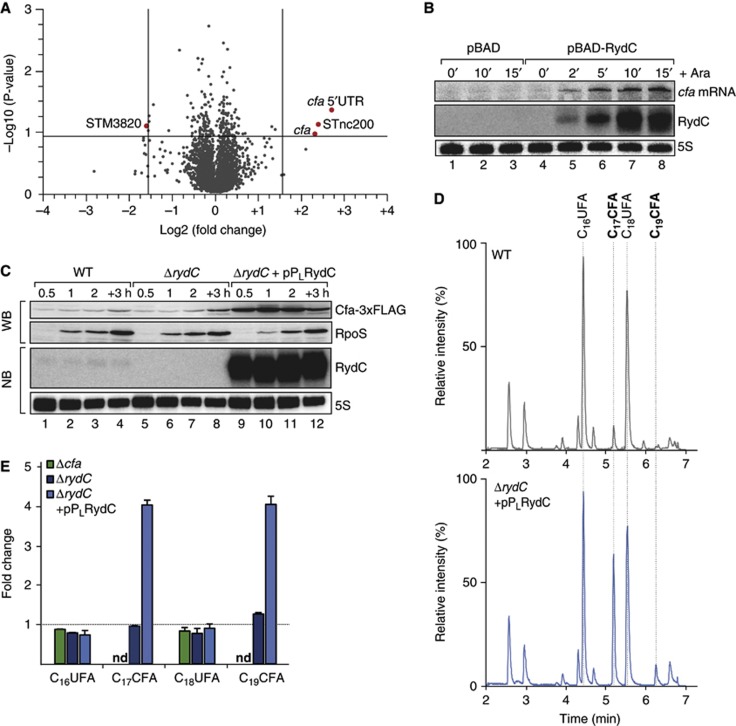
RydC induces cfa expression and activity. (A) Microarray analysis of Salmonella genes affected by pulse overexpression of RydC. RydC expression was induced by addition of arabinose (final concentration: 0.2%) to rydC mutant cells carrying pBAD-RydC or control plasmid pBAD. Changes in transcript abundances were scored on Salmonella-specific microarrays; genes displaying >3-fold change (P-value<0.15) are marked in red. (B) RydC and cfa mRNA levels were determined on northern blots of total RNA extracted from rydC mutant cells carrying plasmids pBAD or pBAD-RydC at indicated time points prior to and after addition of arabinose (Ara). The oligo directed against the 5′ UTR of cfa specifically recognizes cfa1 mRNA. (C) Expression of Cfa-3xFLAG in wild-type and ΔrydC mutant Salmonella either carrying a control construct or a plasmid for the constitutive overexpression of RydC from the PL promoter was monitored over growth on western blots. (D) Total ion chromatograms of Salmonella wild-type cells carrying a control plasmid or a ΔrydC mutant transformed with the RydC overexpression plasmid pPLRydC. Cells were grown in M9 minimal medium to exponential phase (OD600 of 0.5), and after alkaline hydrolysis, total fatty acids were analysed by LC/MS. Peaks assigned to C16UFA, C17CFA, C18UFA and C19CFA are indicated. (E) Relative quantification of C16UFA, C17CFA, C18UFA and C19CFA in Salmonella Δcfa or ΔrydC carrying either a control plasmid or pPLRydC. All measurements were normalized to wild type; error bars represent the standard deviation calculated from three independent biological replicates; nd: not detected.
Source data for this figure is available on the online supplementary information page.