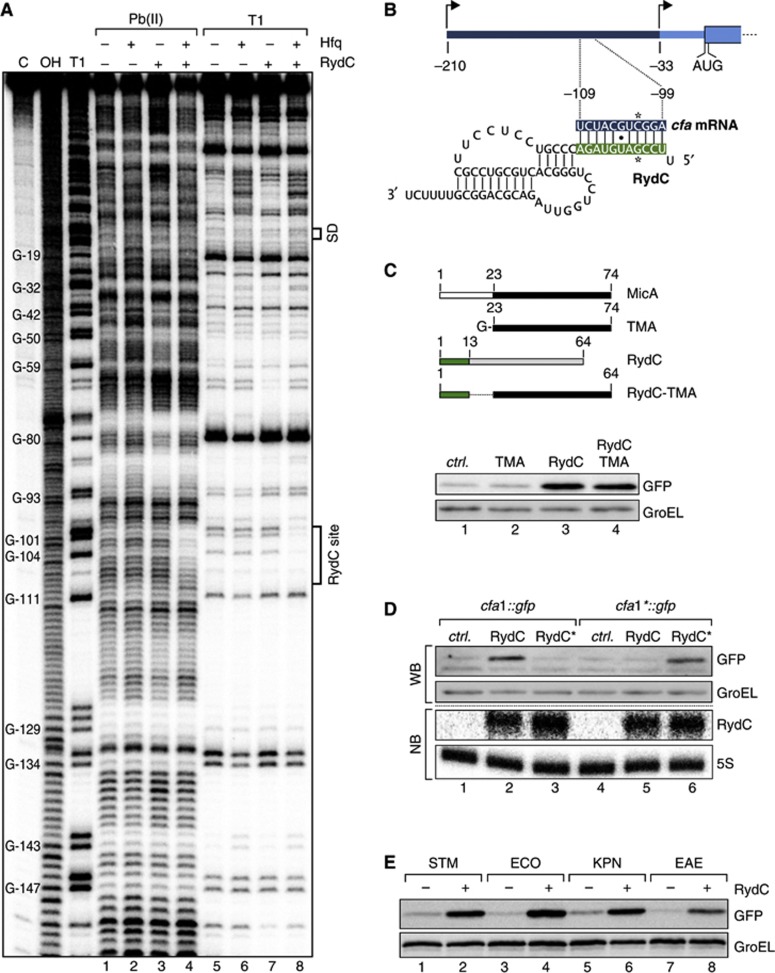
Figure 4.
RydC employs its conserved, single-stranded 5′ end to base pair with cfa1 mRNA. (A) In vitro structure probing using 5′ end-labelled cfa mRNA (TSS1 to nt 70 of the CDS; 20 nM) with lead(II) acetate (lanes 1–4) and RNase T1 (lanes 5–8) in the presence and absence of Hfq (20 nM) and RydC (200 nM). RNase T1 and alkaline ladders of cfa mRNA were used to map cleaved fragments. Positions of G-residues are indicated relative to the translational start site. The RydC binding site and the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) region are marked. (B) Predicted duplex forming between RydC (nts 2–11) and cfa mRNA (nts −109 to −99 relative to the translational start site). Positions of single-nucleotide exchanges generating the compensatory mutants RydC* and cfa* mRNA are indicated. (C) Schematic representation of wild-type MicA and RydC as well as the derivative constructs. The first 13 nts of RydC were fused to the 3′ part of MicA (nts 23–74; TMA) to construct RydC-TMA. The 5′ end of RydC is required to interact with cfa mRNA. GFP levels were determined on western blots of total protein samples isolated from Salmonella ΔrydC ΔrpoS mutants carrying plasmids for cfa1::gfp and either a control or plasmids for PL-driven overexpression of TMA, RydC or RydC-TMA. (D) Validation of the RydC-cfa mRNA interaction. Salmonella ΔrydC ΔrpoS mutants carrying plasmids for cfa1::gfp and cfa1*::gfp in combination with a control plasmid or RydC overexpression plasmids pPLRydC and pPLRydC*. Expression of GFP-fusion proteins was monitored on western blots of total protein samples prepared from cells in exponential growth (OD600 of 1). Equal expression of RydC and RydC* was controlled by northern blot analysis. (E) The regulation of cfa by RydC is conserved. GFP expression was monitored by western blot analysis in Salmonella ΔrydC mutant cells carrying translational Salmonella (STM), E. coli (ECO), K. pneumoniae (KPN) or E. aerogenes (EAE) cfa1::gfp reporter fusions in combination with either a control (−) or a plasmid to overexpress RydC versions of the indicated species (+).
Source data for this figure is available on the online supplementary information page.