Figure 7.
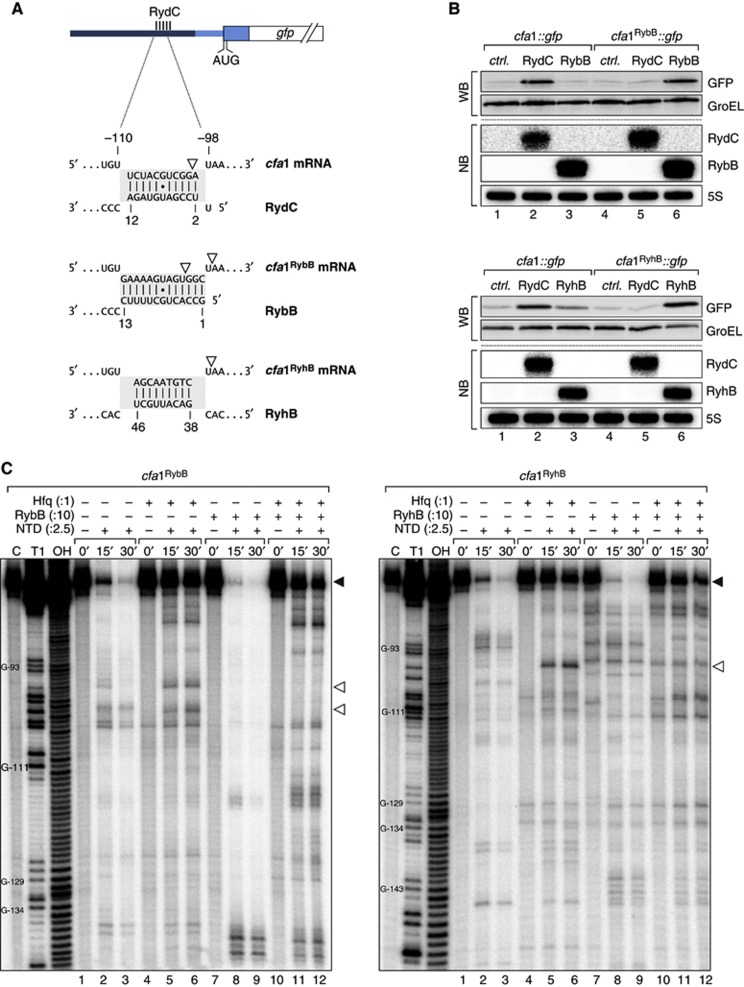
(A) Schematic representation of the base-pairing regions in cfa1, cfa1RybB or cfa1RyhB reporter fusions and the expected base-pairing interactions to RydC, RybB or RyhB, respectively. RNase E cleavage sites identified in in vitro assays are indicated by open arrowheads. (B) The regulation of cfa expression is independent of the actual seed sequence. Salmonella ΔrydC ΔrybB or ΔryhB mutants were transformed with cfa1::gfp and either cfa1RybB::gfp or cfa1RyhB::gfp reporter fusions, respectively. GFP levels were determined by western blot analysis in the presence of either a control plasmid or constructs to constitutively overexpress RydC, RybB or RyhB. See Supplementary Figure S9 for quantification. Expression of RydC, RybB and RyhB sRNAs was monitored on northern blots. (C) Determination of cfa1RybB (left panel) and cfa1RyhB (right panel) cleavage sites in vitro. Time-course experiment of RNase E-mediated decay of cfa1 variants as described in Figure 6C but using cfa1RybB or cfa1RyhB RNA and RybB or RyhB sRNAs, respectively. Mapping of the cleavage intermediates indicated by an open arrowhead is marked in (A).
Source data for this figure is available on the online supplementary information page.