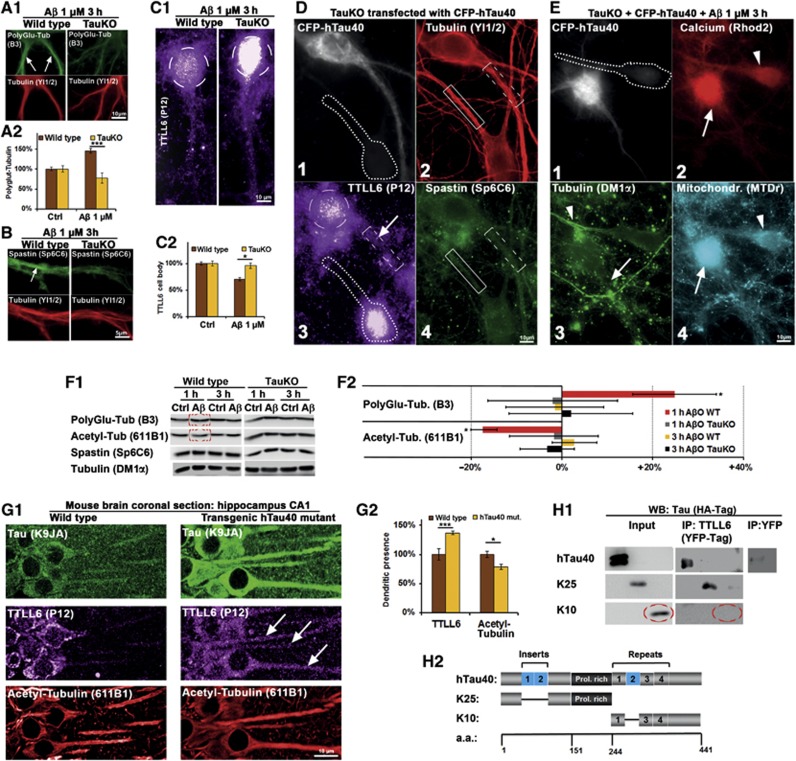
Figure 7.
Tau deficiency prevents AβO-induced polyglutamylation, spastin recruitment, and TTLL6 transport into dendrites. Transfection of human Tau causes TTLL6 transport into dendrites and re-establishes AβO toxicity in TauKO cells. (A–C) Primary wt and TauKO hippocampal neurons aged 19–20DIV were treated with Aβ (1 μM, 3 h) and stained as indicated. (A1) In wt cells (left panels), Aβ treatment results in increased dendritic polyglutamylation (arrows). In TauKO cells (right panels), polyglutamylation of MTs remains at baseline levels after Aβ exposure. (A2) Quantification of (A1). (B) After Aβ exposure, spastin is recruited to MTs in the case of wt cells (left panels, arrow), but not in TauKO cells (right panels). (C1) After Aβ exposure, TTLL6 is reduced in the soma (circle) in the case of wt cells (left panel) compared to TauKO neurons (right panel). (C2) Quantification of TTLL6 levels in the cell body shows reduction in TTLL6 of wt cells. (D) Transfection of CFP-hTau40 results in translocation of TTLL6 from the soma into the dendrite, but no spastin recruitment and no loss of MTs. (1) CFP signal indicates transfected cell, neigbouring cell (dotted line) is not transfected. (2) Transfection of Tau does not change MT density (boxes indicate dendritic segments; transfected cell: dotted box; untransfected cell: solid box). (3) Tau-transfected cell shows translocation of TTLL6 into the dendrite (boxed; arrow); also note the reduction in the cell body (circle), while in the untransfected cell (dotted line) TTLL6 remains in the cell body. (4) Staining of spastin; Tau transfection does not change spastin recruitment. (E) Presence of Tau and AβO insult are necessary for MT loss, Ca++ rise, and clustering of mitochondria. TauKO cells were transfected with CFP-hTau40 for 3 days and then treated with Aβ 1 μM for 3 h. (1) TauKO cell transfected with CFP-hTau40 shows the CFP signal, neighbouring untransfected cell is indicated by dotted line. (2) Tau-transfected cell (arrow) shows strong Ca++ increase compared to untransfected cell (arrowhead). (3) Tau-transfected cell shows MT loss (arrow), while neighbouring cell displays normal MT density (arrowhead). (4) Tau-transfected cells show mitochondria clustering in the cell body (arrow) compared to untransfected cell (arrowhead). (F1) Western blot analysis of primary neurons shows an increase in polyglutamylation of microtubules, and a decrease in acetylation of microtubules only in wild-type neurons after 1 h of Aβ treatment, but no change after 3 h and no change in TauKO neurons, and no change in spastin or tubulin levels. The same membranes were used for polyglutamylation and acetylation of microtubules. (F2) Quantification of (F1). (G) Coronal sections of the CA1 region of the hippocampus of wild-type mice (left panels) and transgenic mice expressing human Tau (right panels) were stained for Tau with an antibody that detect both mouse and human Tau, TTLL6 and acetylated tubulin as a marker for stable microtubules. (G1) Upper panels: compared to wild-type mice, transgenic mice express more Tau; Tau is also strongly missorted into the somatodendritic compartment. Middle panels: in wild-type mice, TTLL6 is present mainly in the cell body, in transgenic mice it is also sorted into the dendrites (arrows). Lower panels: transgenic mice show lower levels of acetylated microtubules. (G2) Quantification of (G1). (H) HEK293 cells were transfected with HA-tagged versions of the longest human Tau isoform (hTau40), or the N-terminal half lacking both inserts (K25), or the C-terminal half without the second repeat (K10), plus TTLL6-YFP or YFP alone. (H1) Immunoprecipitation with an antibody against YFP pulled down hTau40 and K25, but not K10 in the case of TTLL-YFP transfection, while YFP alone did not pull down hTau40. Western blotting was done with an antibody against HA-Tag. (H2) Constructs used for the IP reveal that the presence of the C-terminal half, including the repeat domain, and both inserts in the N-terminal half are not required for binding of TTLL6 to Tau.