Fig. 6.
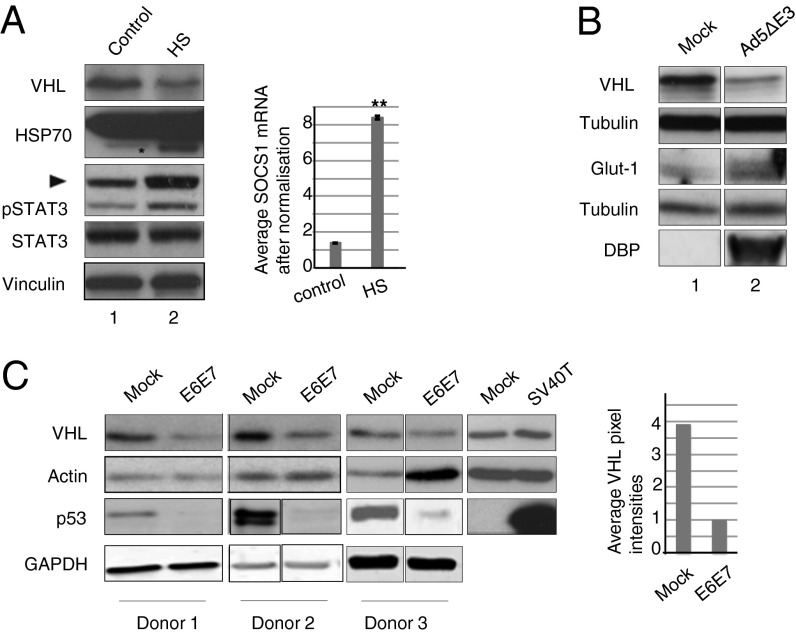
Heat shock and viral infection decreases VHL protein. (A) Tet-on inducible HeLa cells were subjected to heat-shock treatment (HS) or kept at 37 °C as control. VHL protein decrease upon heat shock, as shown in the representative IB, is significant and consistent (P < 0.05, n = 3). Control: Hsp70 asterisk indicates the stress-induced band. A graphical representation of SOCS1 mRNA in control and HS cells shows a statistically significant (P < 0.006, n = 3) and reproducible increase of SOCS1 mRNA. (B) HeLa cells were either mock infected or infected with Ad5ΔE3. Twenty-four hours after infection, lysates were probed for VHL and Glut1. Infection was confirmed by probing with DBP. Loading control: Tubulin. (C) Primary Human Keratinocytes expressing viral proteins (SI Materials and Methods). Lysates were probed for p53 and VHL protein. Loading control: GAPDH.