Fig. 2.
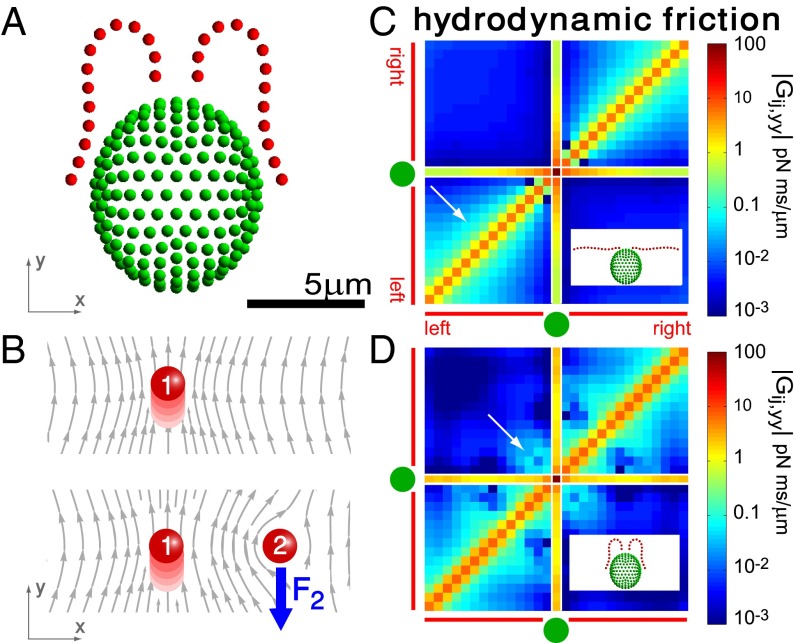
Hydrodynamic interactions between the two flagella are weak. (A) Model Chlamydomonas cell represented by an ensemble of 300 spheres used to compute hydrodynamic friction forces at low Reynolds numbers. In our calculations, the model cell was assumed to be far from any surfaces. (B) Illustration of hydrodynamic interactions between spheres. A single sphere (labeled 1) moving with velocity 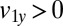 along the y axis will drag fluid alongside and thus exert a total hydrodynamic friction force
along the y axis will drag fluid alongside and thus exert a total hydrodynamic friction force 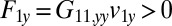 on the fluid. If a second sphere (labeled 2) is held fixed close to the first one, it will locally slow down this fluid flow. The force
on the fluid. If a second sphere (labeled 2) is held fixed close to the first one, it will locally slow down this fluid flow. The force 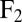 required to hold the second sphere equals the force exerted by this sphere on the fluid; its y component
required to hold the second sphere equals the force exerted by this sphere on the fluid; its y component 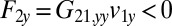 defines a friction coefficient
defines a friction coefficient 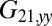 that characterizes hydrodynamic interactions between the two spheres. (C) Hydrodynamic interactions between different parts of the model cell. Analogous to B, one defines a matrix
that characterizes hydrodynamic interactions between the two spheres. (C) Hydrodynamic interactions between different parts of the model cell. Analogous to B, one defines a matrix 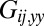 of hydrodynamic friction coefficients for the ensemble of
of hydrodynamic friction coefficients for the ensemble of 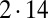 flagellar spheres and the rigid sphere cluster constituting the cell body that together represent a Chlamydomonas cell (Inset). Each column of the color-coded matrix shows the magnitude of hydrodynamic friction exerted by a flagellar sphere (or the cell body), if a single sphere or the cell body is moved parallel to the long cell body axis. Off-diagonal entries characterize hydrodynamic interactions, which are particularly pronounced along a single flagellum (white arrow), or between one flagellum and the cell body (central column). Hydrodynamic interactions between the two flagella are very weak and partly screened by the cell body. (D) Same as in C, but for a recovery stroke configuration. There are weak hydrodynamic interactions between the proximal segments of the two flagella (white arrow). All friction coefficients shown scale with the viscosity of the fluid, which was taken as the viscosity of water at 20 °C,
flagellar spheres and the rigid sphere cluster constituting the cell body that together represent a Chlamydomonas cell (Inset). Each column of the color-coded matrix shows the magnitude of hydrodynamic friction exerted by a flagellar sphere (or the cell body), if a single sphere or the cell body is moved parallel to the long cell body axis. Off-diagonal entries characterize hydrodynamic interactions, which are particularly pronounced along a single flagellum (white arrow), or between one flagellum and the cell body (central column). Hydrodynamic interactions between the two flagella are very weak and partly screened by the cell body. (D) Same as in C, but for a recovery stroke configuration. There are weak hydrodynamic interactions between the proximal segments of the two flagella (white arrow). All friction coefficients shown scale with the viscosity of the fluid, which was taken as the viscosity of water at 20 °C, 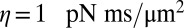 .
.