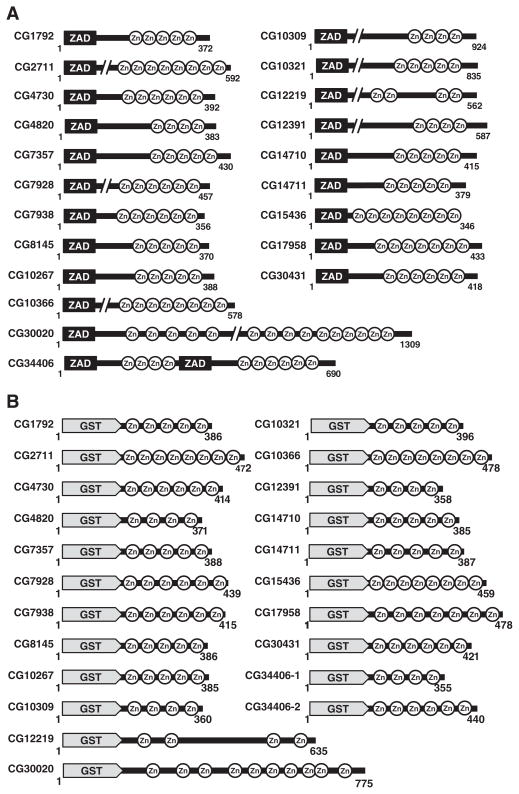
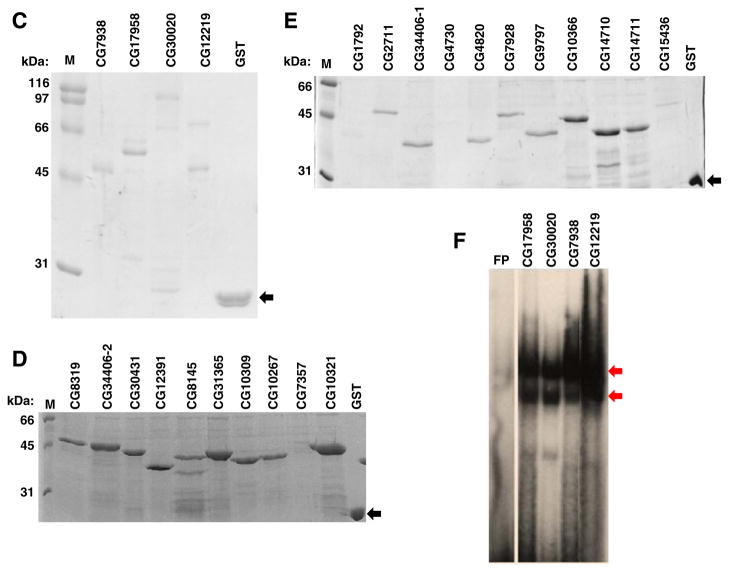
Fig. 1.
ZAD-ZFPs and GST-ZnF recombinant proteins: (A) schematics of the natural architecture of 21 ZAD family members (Section 1). (B) Diagrammatic representation of 22 GST-ZnF recombinant plasmids constructed from 21 ZAD members. Purified GST-ZnF recombinant proteins are shown for the first four (C), an additional ten (D), and another eleven (E) ZAD family members along with broad range protein marker (M), and purified GST affinity tag as control (indicated by black arrows) (panels D and E also contain GST-ZnF proteins of CG8319, CG9797 and CG31365 that were not considered further as mentioned in Section 3.2). (F) Binding site selection and EMSA. Purified GST-ZnF recombinant proteins were bound to an end labeled 49-mer oligonucleotide library. Representative binding for four ZAD members are shown. Red arrows indicate the shifted DNA–protein complexes.