Figure 2.
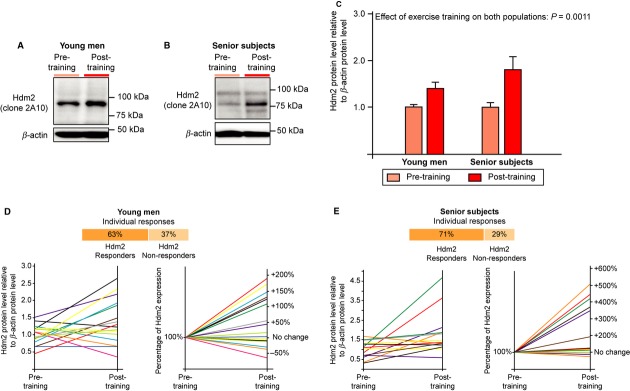
Exercise training increases expression of human double minute-2 (Hdm2) protein in human skeletal muscle. (A and B) Representative immunoblots of Hdm2 protein expression in the vastus lateralis muscle from young men (A, n = 16) or senior subjects (B, n = 14) before and after endurance training. C, Densitometric analysis of Hdm2 protein expression is represented and β-actin was used as a loading control. Data are presented as means ± SEM. The effect of exercise training or age was considered statistically significant when P ≤ 0.05 after two-way ANOVA analysis and Bonferroni posttest. (D and E) Representation of individual responses to training for Hdm2 protein expression in muscles from young (D, n = 16) and senior subjects (E, n = 14). Individual responses are expressed as raw values (Hdm2 normalized to β-actin, top graph) and in percentage of change from pretraining (bottom graph). For each population, the percentages of Hdm2 responders (i.e., subjects having an increased expression of Hdm2 in response to training) and nonresponders are indicated.
