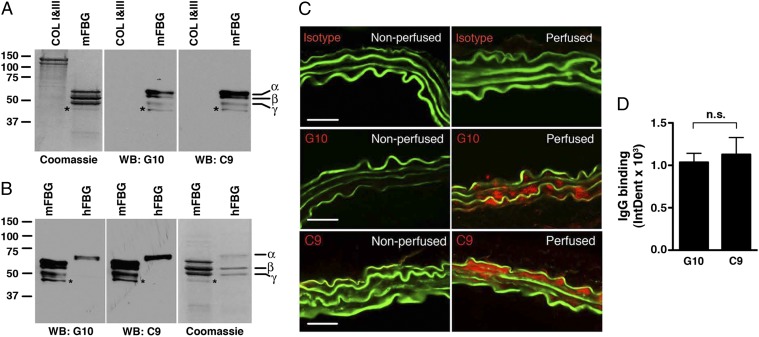
Fig. 2.
Cloning of anti-fibrinogen antibodies. Screening of hybridoma clones using mouse fibrinogen as an antigen identified two mAbs, G10 and C9, that recognize different chains of mouse fibrinogen (mFBG) (A) and human fibrinogen (hFBG) (B) but not mouse types I and III collagen (COL), as determined by Western blot (WB) analysis. *Minor band that likely represents degradation product of one of the major chains. Coomassie-blue stained gel served as protein loading control. (C) G10 and C9 mAbs bind to elastase-perfused aortic wall. μMT mice were left nonperfused (negative control) or perfused with elastase followed by i.v. transfer of 250 μg of IgG isotype control or the indicated mAb. Thirty minutes after perfusion, aortas were harvested and bound mAbs were detected with an anti-mouse IgG (red). The elastic fibers are autofluorescent (green). Representative photomicrographs are shown. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (D) Quantitative analysis of G10 and C9 binding to abdominal aortas 30 min after elastase perfusion and mAb transfer. n = 3 aortas per treatment, six to nine sections per aorta. The mean integrated OD (IntDen) ± SEM per aortic cross-section was calculated as detailed in Materials and Methods. NS, not significant.