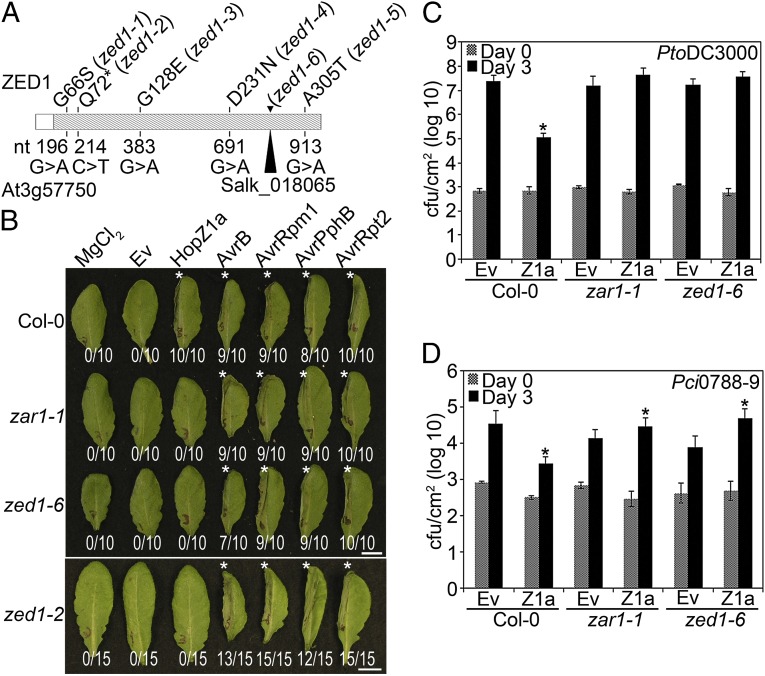
Fig. 1.
zed1 mutants are affected in the predicted kinase domain, are specifically impaired in the recognition of HopZ1a, and exhibit increased virulence of HopZ1a. (A) ZED1 sequence schematic, with hatched region representing the predicted kinase domain. The nucleotide changes identified in the EMS screen are shown below the schematic, whereas the corresponding amino acid mutations are indicated above. The zed1-6 mutation resulted in a premature stop 71 codons after the start codon. The insertion point of the Salk tDNA insertion line is also shown. (B) The left halves of Col-0, zar1-1, zed1-2, or zed1-6 leaves were infiltrated with 10 mM MgCl2 or PtoDC3000 carrying empty vector (Ev), HopZ1a, AvrB, AvrRpm1, AvrPphB, or AvrRpt2. The bacteria were pressure-infiltrated into the leaves at 5 × 107 cfu/mL Photos were taken at 22 h after infiltration. The number of leaves showing an HR is indicated below the leaf. HRs are marked with an asterisk. (C) Col-0, zar1-1, or zed1-6 plants were infiltrated with PtoDC3000 carrying empty vector (Ev) or HopZ1a, and bacterial counts were determined 1 h after infection (Day 0) and 3 d after infection (Day 3). Two-tailed homoschedastic t tests were performed to test for significant differences (*) between Ev control strain and the strain carrying HopZ1a. Error bars indicate the SD from the mean of 10 samples. Growth assays were performed at least three times. (D) Col-0, zar1-1, or zed1-6 were infiltrated with Pci0788-9 carrying Ev or HopZ1a, as in C.