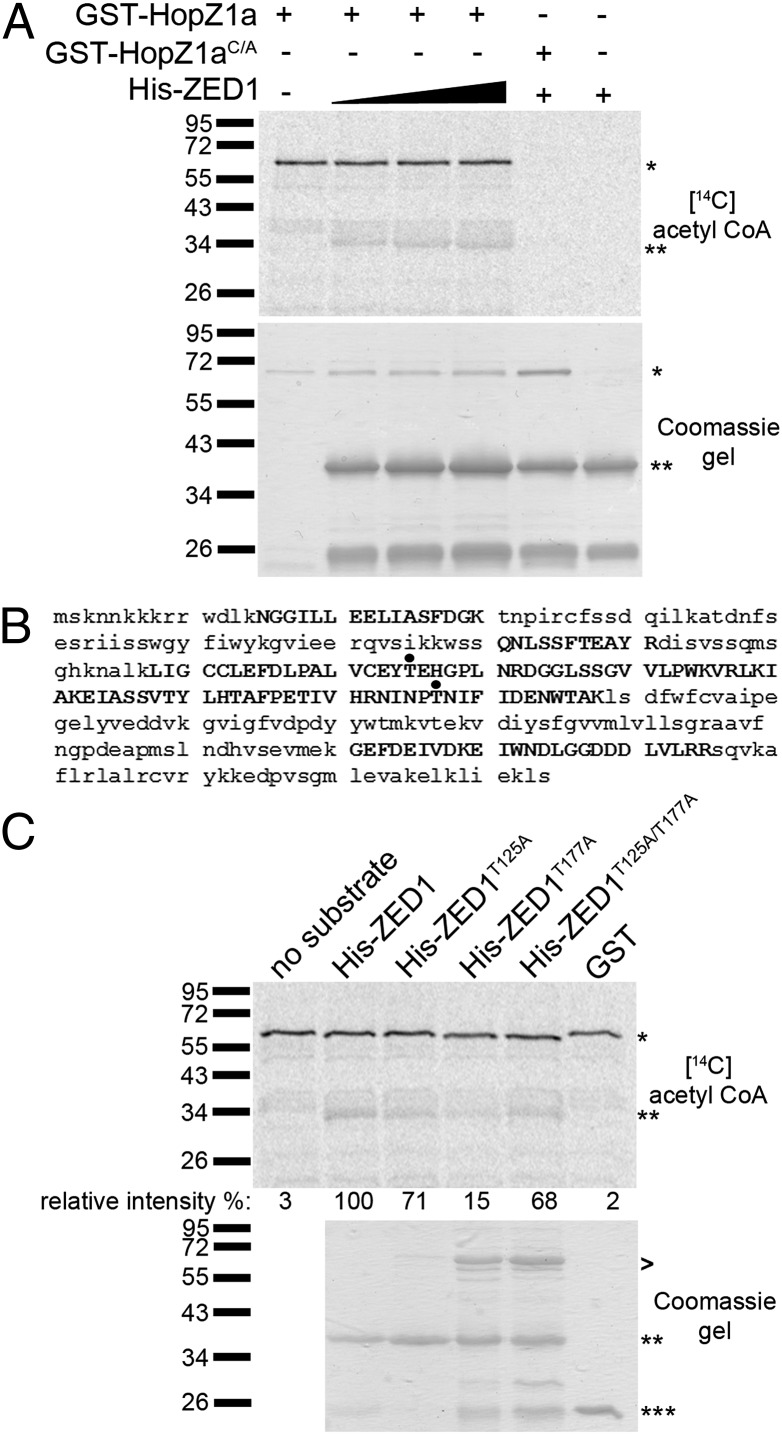
Fig. 3.
HopZ1a acetylates ZED1. (A Upper) Purified GST-HopZ1a or GST-HopZ1aC/A (∼70 kDa) and 6xHis-ZED1 (∼41 kDa) were incubated with phytic acid in the presence of [14C] acetyl-CoA. Samples were separated on a 9% polyacrylamide gel, and 14C incorporation was visualized by Phosphoimager. *, GST-HopZ1a or GST-HopZ1aC/A; **, His-ZED1. (A Lower) Coomassie gel of proteins. (B) LC-MS/MS analysis of immunoprecipitated FLAG-tagged ZED1 proteins in yeast coexpressing ZED1 and HopZ1a. Peptides recovered in LC-MS/MS analysis are shown in capital letters. Acetylated threonines are shown with a black dot. (C Upper) Purified GST-HopZ1a and 6xHis-ZED1, 6xHis-ZED1T125A, 6xHis-ZED1T177A, or 6xHis-ZED1T125A/T177A were incubated with phytic acid in the presence of [14C] acetyl-CoA. Samples were separated on a 9% polyacrylamide gel, and 14C incorporation was visualized by Phosphoimager. *, GST-HopZ1a; **, His-ZED1 or mutants; ***, GST. The signal intensity for each 14C-labeled band was quantified by using ImageJ and is shown below the Coomassie gel. The maximum signal intensity was arbitrarily set at 100% for wild-type His-ZED1, and other signal intensities are relative to this value. (C Lower) Coomassie gel of His-ZED1, His-ZED1 mutant, and GST proteins as a loading control. GST-HopZ1a is loaded as shown in A. >, contaminating proteins in the protein preparation.