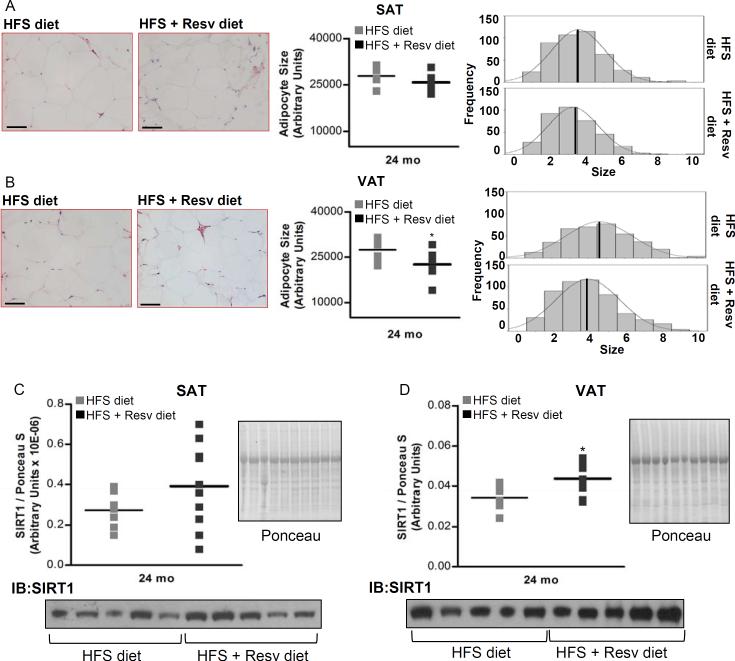
Figure 2. see also Figure S3. Resveratrol decreases mean adipocyte size and increases SIRT1 protein expression in visceral WAT of rhesus monkeys maintained on HFS diet for 2 years.
(A) Morphologic characteristics of subcutaneous WAT. (B) Morphologic characteristics of visceral WAT. (C) SIRT1 protein levels in subcutaneous WAT. (D) SIRT1 protein levels in visceral WAT. (A and B) H&E-stained sections of WAT from monkeys fed HFS and HFS + Resv diet are shown. Images were captured at 20× magnification. Scale bar: 200 μm. Mean adipocyte size and adipocyte frequency distribution show cell surface areas in both fat depots after 24-mo of dietary intervention. (A to D) Results are expressed in a dot plot format, which represents the individual data and the mean. (A) n=7 (HFS diet); n=8 (HFS + Resv diet). (B) n=8 for each group. (C and D) n=10 for each group. The data were analyzed using Independent-Samples t test to analyze statistical significance between HFS vs. HFS+Resv diet at 24-mo of dietary intervention. *, P < 0.05 (HFS vs. HFS + Resv diet). HFS: high-fat, high-sugar; Resv: resveratrol; VAT: visceral adipose tissue; SAT: subcutaneous adipose tissue.