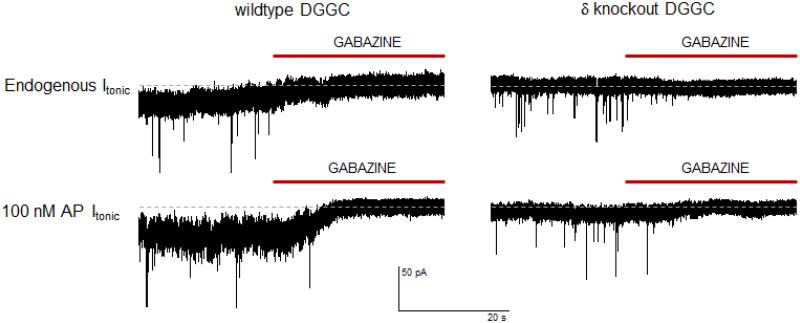
Fig. 8. Comparative analysis of allolpregnanolone potentiation of tonic currents in wildtype and δ-subunit knockout mouse hippocampus slices.
Tonic current recordings were made from DGGCs in 300 μM slices at —65 mV voltage-clamp recording. ACSF perfusion contained tetrodotoxin, AP5 (2R-amino-5-phosphonopentanoate), and DNQX (6,7-dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione) to block voltage-gated Na+ channels and glutamatergic currents to isolate GABAergic signal. No exogenous GABA or GABA transport blocker was included in this perfusion preparation. After holding current level was established in the presence of no endogenous GABAergic agent or 100 nM allopregnanolone, 50 μM gabazine (SR-95531) was applied to block all GABAa receptor currents. Root mean square noise is reduced and phasic IPSCs are blocked in the presence of gabazine in DGGCs. A noticeable shift in tonic conductance is observed in wildtype but not in δ knockout DGGCs. The gray dotted line indicates the mean holding level upon gabazine blockade of tonic current.