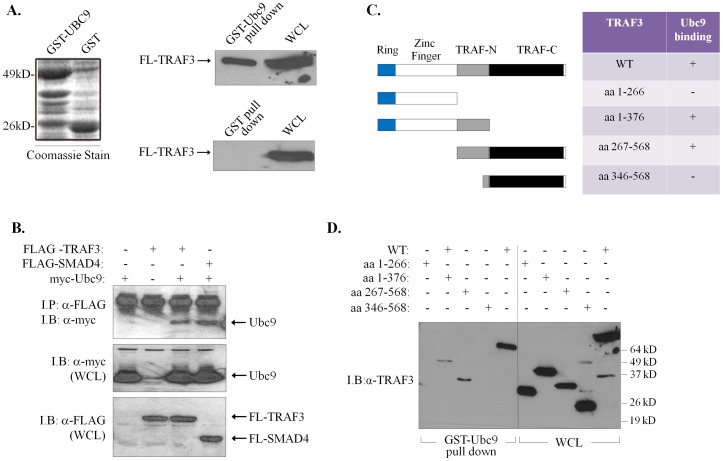
Figure 2. TRAF3interacts with Ubc9 through its ring finger TRAF-N domain.
(A) GST-Ubc9 produced in bacteria as fusion with GST interacts with FLAG-tagged TRAF3 expressed in HEK 293 cells. GST or GST-Ubc9 was incubated with protein lysates isolated from FLAG-TRAF3 transfected HEK293 cells. Pulled-down proteins were solubilized in SDS protein sample buffer, separated on 8% SDS polyacrylamide gels and immunoblotted for TRAF3. Coomassie blue staining was used to confirm equal utilization of GST and GST-Ubc9 proteins in the pull-down assays. (B) Ubc9 and TRAF3 interact in vivo. FLAG-tagged TRAF3 was co-expressed with myc-tagged Ubc9 in HEK293 cells. Ubc9 was detected in anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates. As positive control [25], FLAG-tagged SMAD4 was used to monitor interactions with Ubc9. (C &D) Interaction of TRAF3 deletion mutants with Ubc9 in an in vitro GST pull-down assay. 293T cells were transiently transfected with the FLAG-tagged TRAF3 deletion mutants shown in C. Thirty six hours later, the extracts were incubated with purified GST-Ubc9 bound to glutathione sepharose beads. Interacting proteins were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-FLAG mAb (lanes 1-5; D). Whole cell lysates (30 µg) were analyzed in parallel to monitor the motility of the TRAF3 deletion mutant proteins (lanes 6-10). I.P.; immunoprecipitation. I.B.; immunoblot. WCL; Whole cell lysates